 |
|
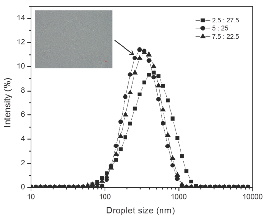
The effect of continuous phase composition and microfluidization pressure on properties of chia oil emulsions was analyzed using a D-optimal combined design. The results indicated that the suggested models were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) fitted for all response variables (emulsion droplet size, ζ-potential, Turbiscan stability index and apparent viscosity) and showed high coefficients of determinations (0.897 - 0.933). The soy protein isolate had the major effect on the evaluated parameters due to their emulsifying property and electrical charge. The microfluidization technology allowed the production of emulsions with a droplet size in the range of nanometers (< 500 nm) and monomodal particle size distribution. The optimum condition to obtain the minimum emulsion droplet size (300.97 nm), ζ-potential (-40.03 mV), Turbiscan stability index (1.06) and apparent viscosity (18.65 mPa•s) was when a chia oil emulsion was formulated with 4.8 % w/w of SPI and 25.2 % w/w of MD, applying high microfluidization pressure (104 MPa).
Keywords: Soy Protein Isolate, Maltodextrin, Microfluidization, Emulsion stability, D-optimal combined design, Chia oil.
|
|
 |

