 |
|
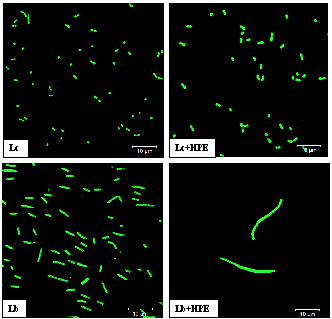
The effects of habanero pepper extract on Staphylococcus aureus, Lactobacillus casei Shirota and Leuconostoc citreum were studied. The extract contained 8.71 mg/g of capsaicin and 4.72 mg/g of dihydrocapsaicin as well as minor concentrations of gallic, chlorogenic, caffeic, p-coumaric acids and quercetin, determined by HPLC. Inhibition of S. aureus at 4 h was observed with a death rate of -1.53 h-1. While, L. casei Shirota showed a survival of 4.15x105 CFU/mL and L. citreum of 2.20x105 CFU/mL. When L. casei Shirota was exposed 12 h to the MRS-50% extract, an elongation of the cells was observed and the Feret´s diameter increased from 3.3 to 21.6 µm; showing blistering on the cell surface. Regarding to L. citreum, an increase of 70% in cell area was observed, maintaining its circularity; also showed an improve in mucin adhesion ability of 4.42x105 CFU/mL, increasing its survival to bile salts by 85% and the synthesis of L36 ribosomal protein, corroborating the presence of rpmJ gene that encodes for this protein.
Keywords: Leuconostoc citreum, Lactobacillus casei Shirota, Staphylococcus aureus, Capsaicinoids, Morphostructure, Functional properties.
|
|
 |

