Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 18, No. 1 (2019), Mat128
Dispersion of carbon nanotubes and their influence for ozone monitoring
|
S. Capula-Colindres, G. Terán, E. Torres-Santillan, L. Villa-Vargas, J.C. Velázquez
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Mat128
Abstract
 |
|
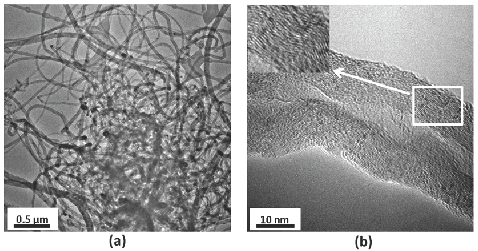
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) are promising material to be used as sensitive materials in the gas detection. One disadvantage is their insolubility in different media which limits their performance and processing. By employing techniques not covalent with surfactants is possible increase dispersion of CNT. This article reports the results found in the detection of ozone using pristine multi-walled carbon nanotubes dispersed in three different media: deionized water, methanol and glycerol. Materials dispersed in deionized water exhibited a zero detection of ozone at different concentrations studied. In comparison, electronic devices where sensitive materials were dispersed with methanol and glycerol showed a change in resistance depending on concentration and operating temperature evaluated. The best response was found to be at high temperatures (120 -200 °C). The materials have been characterized by high resolution transmission electron microscopy and optical microscopy technique
Keywords: dispersion, surfactant, multi-walled carbon nanotubes, ozone, sensor.
|
|
 |

