 |
|
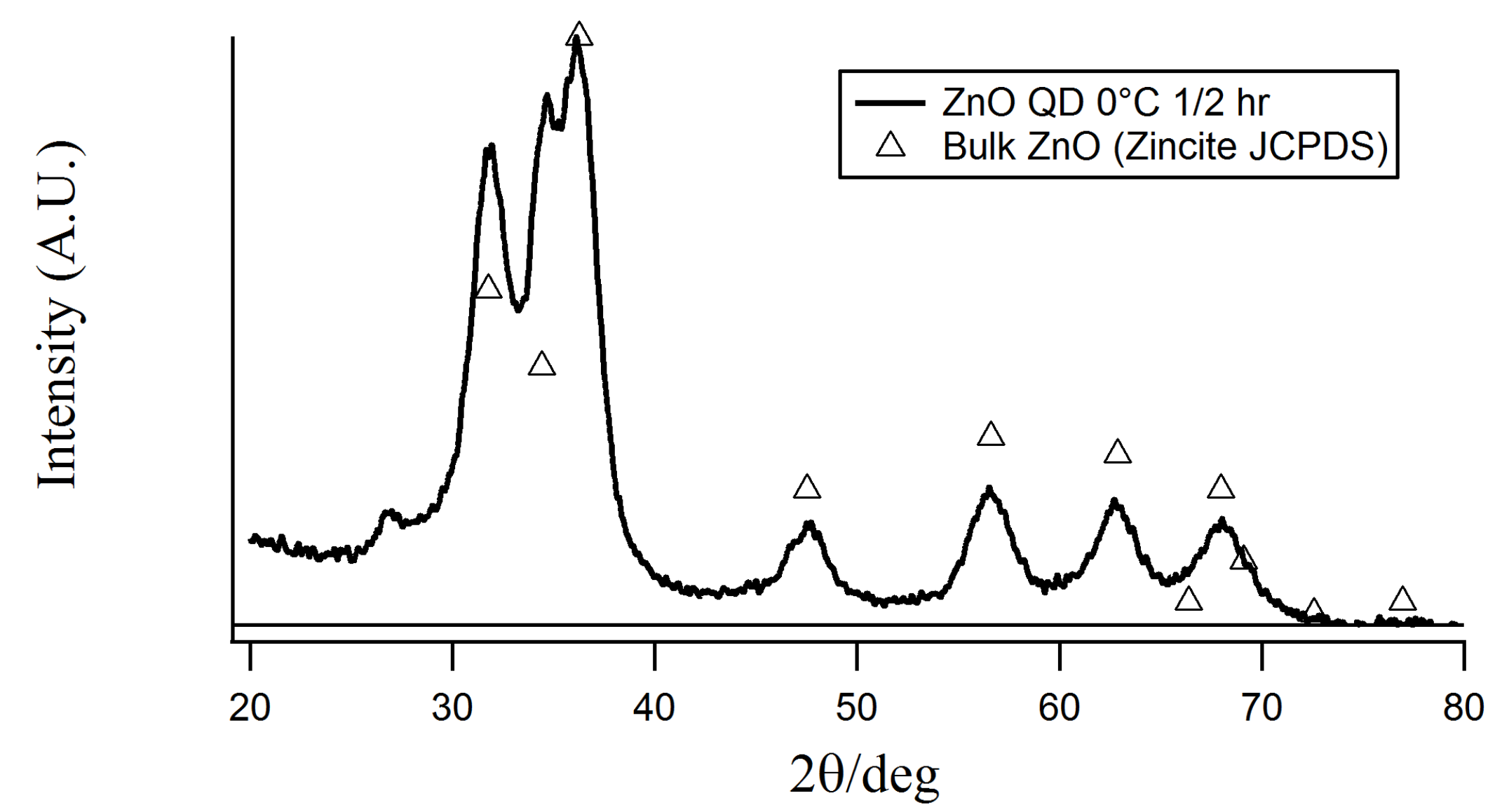
In this work, the mechanical properties at equilibrium of two dimensional layers made by ZnO Quantum dots deposited at the air/water interface were studied. ZnO nanoparticles were synthesized by the sol-gel method and their functionalization was made by the hydrolytic silanization method. Their mechanical properties were evaluated using a Langmuir trough equipped with a Du Noüy-Padday rod. With this technique, isotherms, compression modules and hysteresis cycles of the system were obtained. Our results showed that partially hydrophobic particles form two dimensional soft solids at the air/water interface, reaching values of their adiabatic compression modulus corresponding to a liquid condensed phase when they are compressed above surface concentrations of the order of 1x101 mg/m2. Nanoparticle layers presented dependence with the rate of compression and significant hysteresis, showing their complex behavior. Layers did not present collapse, but a semi constant value of the pressure upon high surface concentrations was observed, an indicative of the high adsorption energy of the nanoparticles. The mechanical properties reported, make these particles suitable for further applications on the stabilization of aqueous foams.
Keywords: ZnO, Quantum Dot, Particle Monolayer, Isotherms, Compression Modulus.
|
|
 |

