Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 18, No. 2 (2019), Alim209
Sorption behavior of citric pectin films with glycerol and olive oil
|
J.G. Hernández-Carrillo, H. Mújica-Paz, J. Welti-Chanes, A.S. Spatafora-Salazar, A. Valdez-Fragoso
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Alim209
Abstract
 |
|
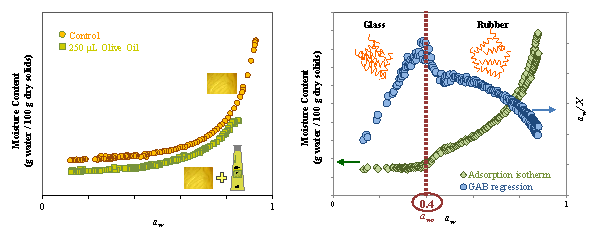
The effect of glycerol and olive oil on water sorption isotherms of orange (FOP) and grapefruit (FGP) peel pectin films was studied. Additives decreased the equilibrium moisture content (X) and the extent of the observed hysteresis. Abrupt changes in the adsorption isotherms of the films were noted, and were very well correlated to one of the maxima of the second derivative of X as function of aw. Converted adsorption data for GAB regression (aw/X) generated curves with a sharp peak, linked to the isotherms inflection points. aw/X vs aw diagrams were valuable to identify order–to-disorder transitions in pectin films. Glycerol concentration reduced the critical water activity in FGP. GAB model described adsorption isotherms above the transition (R2 > 0.932), and Halsey model exhibited a better fit (R2 > 0.984). Desorption phenomena was better described by Peleg model (R2 > 0.959).
Keywords: citric pectin; edible films; sorption isotherms; glass transition; second derivative.
|
|
 |

