 |
|
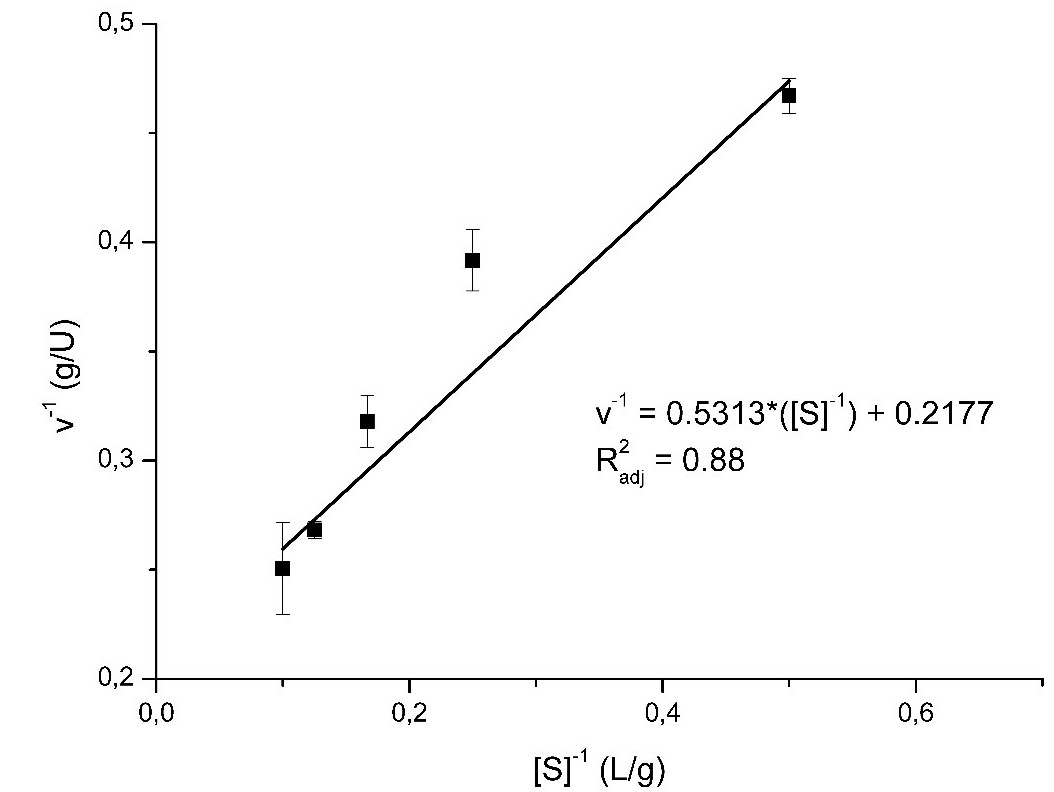
To investigate the potential of the jackfruit seed residue in xylanase and endoglucanase production, was carried solid-state fermentation by Penicillium roqueforti with this residue, besides was evaluate the filter paper activity of the multienzymatic crude extract obtained. Effects of the independent variables water activity, incubation time and temperature in the responses, xylanase, endoglucanase and FPase activity by means of an experimental design 23. Kinetic parameters of xylanase were also evaluated. At 90% confidence level it was observed that the water activity had no significant effect on the responses since the time and the incubation temperature had significant effects with the exception of the FPase activity where only the time was significant. The best endoglucanase activity was 4.454 U/g and best FPase activity was 0.728 U/g, both obtained at 33°C, 100h and water activity of 0.966, the best xylanase activity was 3.016 U/g obtained at 33°C, 100h and water activity of 0.958. The produced xylanase has Km = 2.44 mg/mL, Vmax = 4.59 U/g and Kcat = 1.57 1/s. Without the use of any inducer, it was possible to obtain endoglucanase and xylanase by solid-state fermentation of jackfruit residue, demonstrating its biotechnological potential as a substrate.
Keywords: multienzymatic complex, jackfruit seed, residues.
|
|
 |

