 |
|
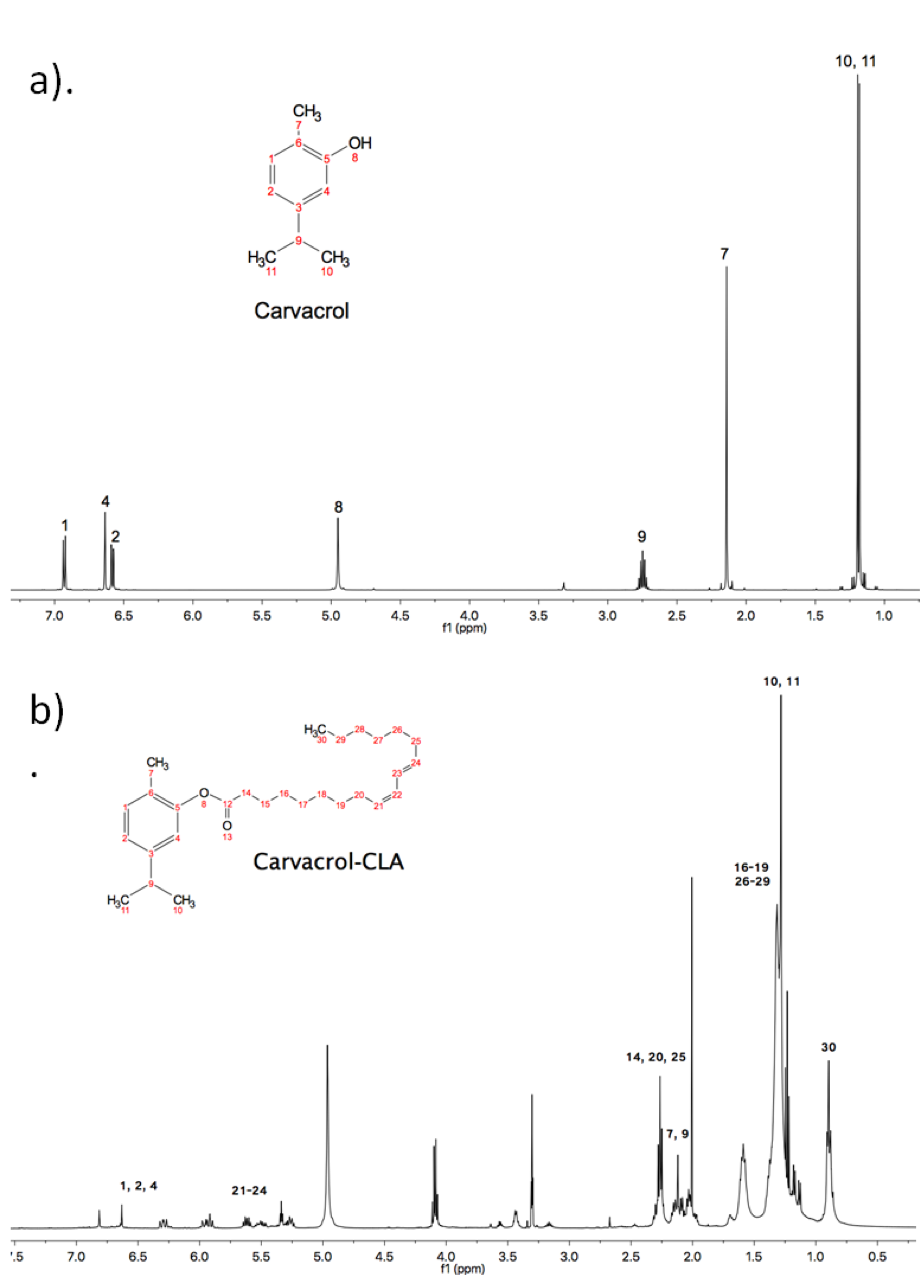
The structure and physicochemical and antioxidant properties of carvacrol, quercetin and vanillin were modified by a lipophilic reaction with conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). The chemical structure of the precursor and lipophilized antioxidants was determined by 1H and 13C NMR. The derivatives of carvacrol-CLA and quercetin-CLA showed the highest yields of lipophilization. The lipophilized systems had greater lipophilicity (clog P, clog S and hydrophilic-lipophilic balance) and greater antioxidant activity than the polyphenol precursors, being the carvacrol-CLA and vanillin-CLA complexes that presented the highest antioxidant activity. The results suggest that the lipophilicization reaction improved the lipophilicity and antioxidant activity of the compounds involved and that these lipophilized derivatives could have applications in the food, cosmetic and medical industries.
Keywords: antioxidant activity, esterification, CLA, hydrophobicity, lipophilicity.
|
|
 |

