 |
|
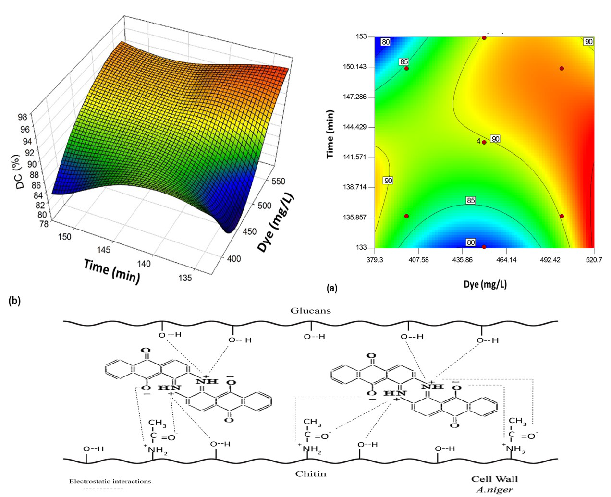
The dumping of dyes into bodies of water represents an environmental and health problem due to its toxicity. A solution to this problem could be the application of mycorremediation. So, in this work Aspergillus niger CDBB-H-175l was investigated in the discoloration (DC) of vat blue dye. A combination of statistical methodologies was applied to optimize DC; initiating with a 24-1 fractional factorial design (FFD), to evaluate; dye concentration, exposure time, pH and agitation. Results showed a minimum and maximum DC of 15% and 43%, respectively. By using a first-order model DC increased further to 63%. Additional experiments enhanced DC to 90% in step 7 of a steepest ascent design, and this was improved to 94% at a higher concentration of 521 mg/L with the application of surface response methodology. Of the 63% total DC determined in the first-order model, 28% was attributed to the glucose oxidase activity (16.5 U/mL) and the H2O2 produced by A. niger, and 72% due to physisorption to the cell wall. This is the first report where H2O2 produced by Aspergillus niger is implicated in dye decoloration.
Keywords: Aspergillus niger, vat blue, discoloration, hydrogen peroxide, optimization.
|
|
 |

