 |
|
The quality of life on Earth is undoubtedly linked to the global quality of the environment. Unfortunately, population growth, environmentally unfriendly industrial processes and the lack of restrictions on the production and use of toxic and/or recalcitrant compounds have led to the release of large amounts of chemical pollutants. Water resources have been particularly affected by the presence of these compounds; furthermore, the conventional wastewater treatment technologies are unable to completely remove the complex mixture of pollutants present in wastewaters. In fact, certain pollutants have been detected in drinking water at concentrations as high as 0.3 μg/L.
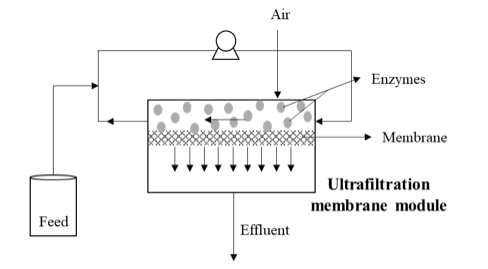
The seriousness of environmental pollution has triggered the development of initiatives and scientific activities for the prevention and control of water pollution; among them, the enzymatic reactors are emerging as a promising alternative.
Keywords: Ligninolytic enzymes, water pollution, endocrine-disrupting chemicals, micropollutants, enzymatic reactors.
|
|
 |

