 |
|
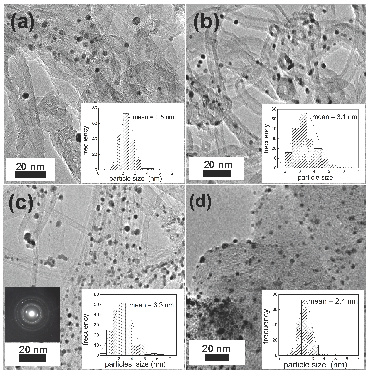
Pt nanoparticles were supported on multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and conventional C-Vulcan XC72 by a vapor-phase impregnation-decomposition method using platinum acetylacetonate as precursor. Both types of carbon supports were impregnated with the precursor vapors at 180 ºC and 3-7 Torr inside a horizontal quartz tube reactor. Then, they were heated at 400 ºC to achieve precursor decomposition and subsequent formation of Pt nanoparticles. Carbon supports, and Pt precursor were mixed in several weight ratios. The Pt content was approximately 5, 10 and 25 wt. %. TEM observations revealed Pt particles ranging from 2.4 to 3.3 nm uniformly distributed on either nanotubes or conventional carbon support. The catalytic activity for nitrate electro-reduction (NER) was investigated in NaNO3 + NaOH solutions using Cycling Voltammetry (CV). The CV measurements showed a redox process from -0.7 to -1.0 V/SCE associated to the nitrate reduction process. It was found that Pt/MWCNTs materials display superior nitrate reduction activity than Pt/C-Vulcan XC72, even the comparable Pt decisive features. The superior activity seems to be associated to the inherent structural features of MWCNTs. Thus, Pt/MWCNTs are attractive materials for electrodes on the nitrate reduction process in alkaline medium aqueous.
Keywords: nanoparticles, platinum, carbon nanotubes, electroreduction, nitrates.
|
|
 |

