 |
|
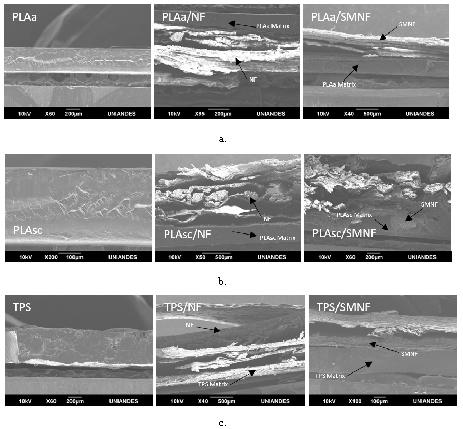
A laminated material was developed using sheets of Polylactic Acid (PLA semicrystalline -PLAsc- and PLA amorphous -PLAa-), and thermoplastic starch (TPS) reinforced with natural fibre (NF) extracted from sheet-stalk of the plantain plant (Musa cavendish). A surface chemical modification of fibres (SMNF) was done in order to improve its compatibility with the polymers. The structural, mechanical, thermal, optical and biodegradation properties were studied. The characterisations show that chemical treatment of fibres increases the tensile strength in the laminates with PLAa, PLAsc and TPS in a 51.4%, 21.4% and 78.1% respectively. Likewise, the elastic modulus was increased by 104%, 57.4% and 124%, respectively. On the other hand, the structural analysis shows that fibres with chemical modification have higher interfacial adhesion to polymers, improving the stability of the materials. Finally, biodegradation tests confirm that the chemical treatment delays the degradation process slightly, but materials comply with international standards for bioplastics. The properties of the laminates could be suitable for the development of trays or other semi-rigid packages for foods.
Keywords: polymer composites, biodegradable polymers, reinforcements, adhesion.
|
|
 |

