 |
|
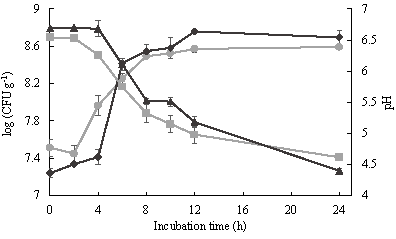
Soy milk is a food rich in proteins, phenolic compounds and lactose-free. However, due to organoleptic and anti-nutritional characteristics, soy milk is not very popular among the population. The objective of this article is to evaluate the changes in the activity of α-galactosidase and β-glucosidase, as well as phytates, isoflavones, phenolic compounds contents and antioxidant activity of soy milk during the fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum BAL-03-ITTG and Lactobacillus fermentum BAL-21-ITTG. Soy milk was fermented for 24 h with L. plantarum and L. fermentum separately, with an increase of 1.2 to 1.4 log CFU g-1 for both strains. The results showed that the strains are able to produce β-glucosidase, carrying out the conversion of β-glucosides in their corresponding aglycones, with an increase of 420 to 490 %. In addition, the strains can decrease approximately 20 % of the content of phytate in soy milk during fermentation. Therefore, both strains could be used in future works to obtain food from fermented soy milk.
Keywords: antioxidants, isoflavones, phytate.
|
|
 |

