 |
|
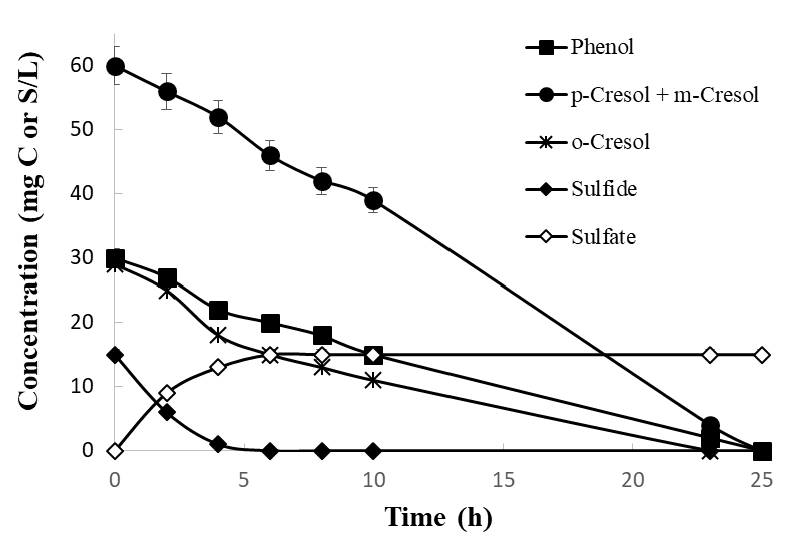
The kinetic and metabolic ability of a nitrifying sludge to simultaneously oxidize ammonium and mixtures of phenol, p-cresol, m-cresol, o-cresol, and sulfide was evaluated throughout the operation cycles of a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). In the nitrifying SBR, it was possible to remove ammonium (150 mg N/L) by nitrification, mineralize the mixtures of phenolic compounds (up to 120 mg C/L), and oxidize sulfide (15 mg S/L) to sulfate. The addition of mixed phenolic compounds and sulfide into the reactor provoked a decrease in specific rates of the nitrifying processes, however, the use of SBR system allowed a decrease of the inhibitory effects along the cycles. The sludge showed a metabolic adaptation to consume the mixtures of phenolic compounds and sulfide throughout the cycles with increasing specific rates of removal. The obtained results showed that the nitrifying SBR can be used for the treatment of wastewaters contaminated with ammonium, mixtures of phenolic compounds, and sulfide.
Keywords: ammonium, mixtures, phenolic compounds, sequencing batch reactor, sulfide.
|
|
 |

