 |
|
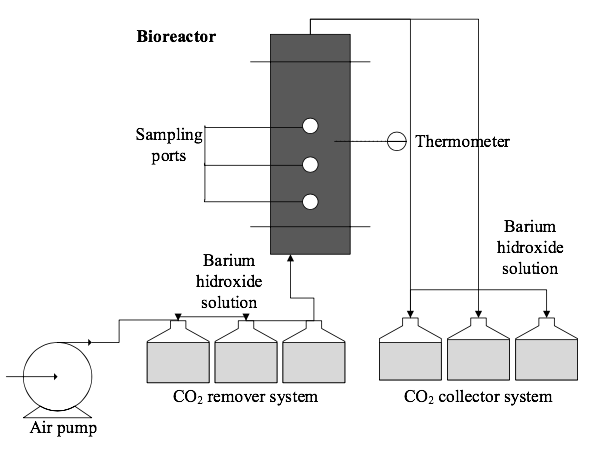
In this study it is reported the treatment of oil-based drill cuttings (OBDC) by the analysis of performance 8 biopiles placed within reactors. Biopiles were prepared with a mixture of drill cutting, bulking agents, microbial consortium, inorganic nutrients and humic acid (HA) solutions at 500, 1,000, 1,500, 2,000, 2,500 and 3,000 mg/L. Experimental follow-up was done registering temperature, CO2 generation and pH. After 8 weeks, oil removal was evaluated using total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) soxhlet extraction, the highest value was 72% removal of TPH obtained with the biopile of 1,500 mg/L of HA. Also, this biopile showed higher temperatures, higher CO2 generation and the lowest pH, indicating a more active biological system compared with other concentrations. The obtained results shows that the addition of HA significantly improves the performance of biopiles, indicating that the combination of technologies employed with addition of HA are effective for the treatment of oil-based drill cuttings.
Keywords: Oil-based drill cuttings, total petroleum hydrocarbons, bioremediation, bioaugmentation, biostimulation, humic acids.
|
|
 |

