Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 18, No. 3 (2019), IA245
Photodegradation of erionyl dye in aqueous medium by sunlight and palladium catalysts
|
G. Pérez-Osorio, F. Hernández-Aldana, J.C. Mendoza Hernández, J. Arriola-Morales, M. Castillo-Morales, S.N. Gutiérrez-Martin, J.M. Gutiérrez-Arias
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/IA245
Abstract
 |
|
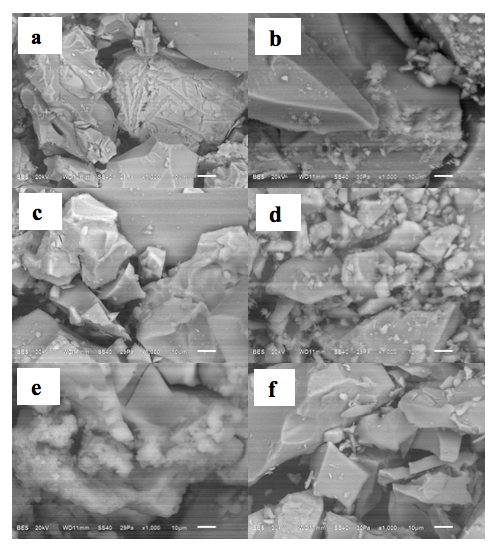
In this investigation, the degradation of blue dye erionyl was evaluated in aqueous medium by photocatalysis with solar radiation. Six catalysts of palladium supported on combinations of aluminum-cerium–zirconium oxides were synthesized by the sol-gel method and impregnation. Materials used as supports were characterized by XRD, meanwhile catalysts were analyzed by SEM and EDS techniques. The Degussa TiO2 commercial was used as reference for evaluating the performance of the palladium catalysts in the photocatalytic processes, since is widely used as an efficient catalyst for photodegradation of pollutants in water. The photocatalytic processes were carryout in a system with borosilicate reactors and high reflectance aluminum foil compound parabolic collectors. The six palladium catalysts achieved a percentage degradation of erionyl blue dye higher than 60%, having the best performance the palladium supported on alumina with 97% degradation after 5 hours of photocatalytic process. It is noteworthy that this catalyst showed a better performance than the TiO2 catalyst reached up to 81% degradation.
Keywords: Photocatalysis, blue dye erionyl, water pollution, solar radiation, palladium catalyst.
|
|
 |

