 |
|
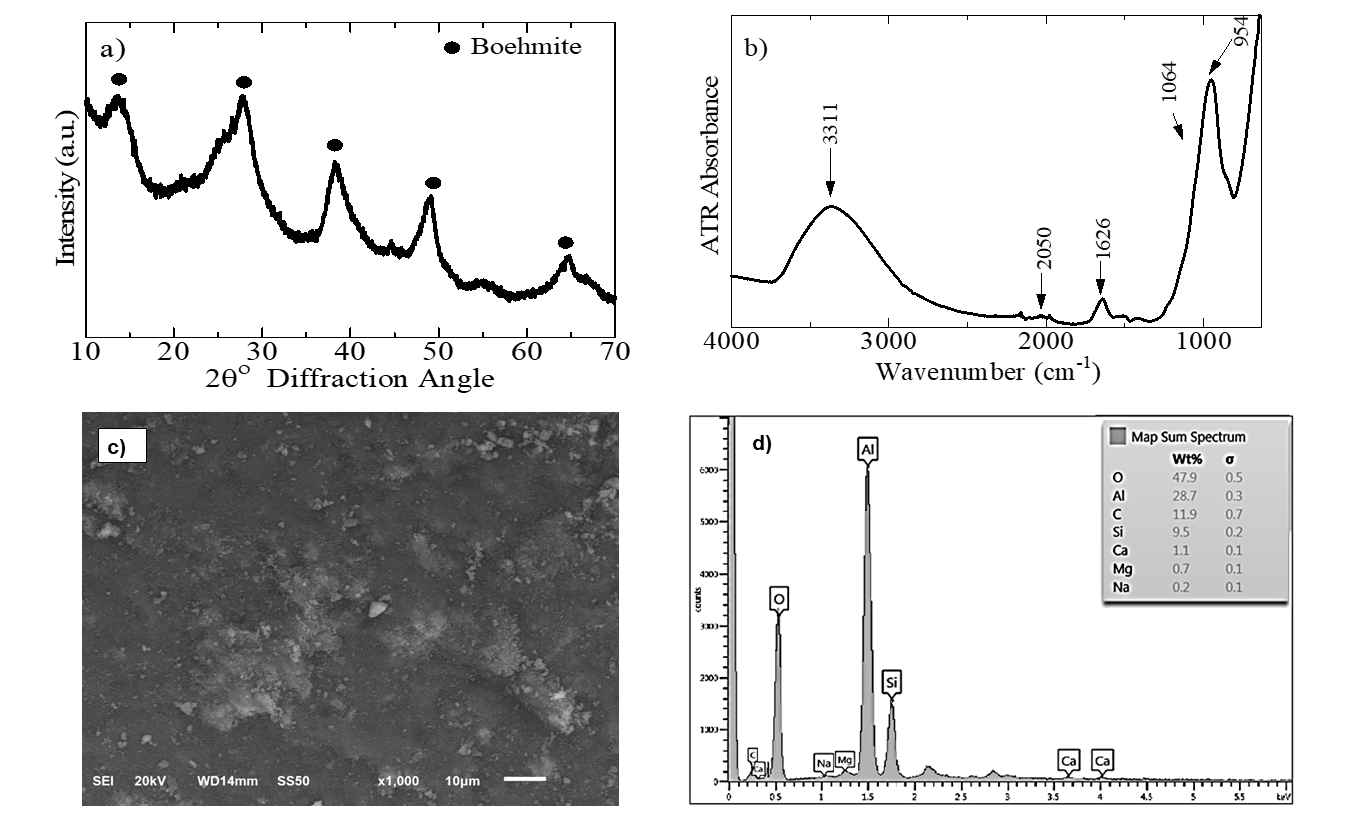
The reuse of a Metal Hydroxide Sludge generated by an electrocoagulation process was used as an adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye in a fixed bed column. The obtained adsorbent was characterized by N2 physisorption, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy-EDS measurements. Continuous column experiments were carried out with a Central Composite Design (CCD) to study parameters such as adsorbent mass (4-8 g), initial concentration of Congo red (20-50 mg·L-1) and feed flow (20-50 mL·min-1) in the breakthrough time, breakthrough volume and saturation time. The high value of the correlation coefficient and the low value of p (< 0.0001) indicates the adequacy of the response surface of quadratic models developed for the variable responses in the optimization process. The capacity of adsorption under conditions optimized in the operation of the column was estimated at 3.57 mg·g-1. In addition, it was found that the Thomas, Bohart-Adams and Yoon-Nelson models adjusted adequately to the column data obtained.
Keywords: adsorption, dye, congo red, EMHS, Central Composite Design, Fixed-bed column.
|
|
 |

