 |
|
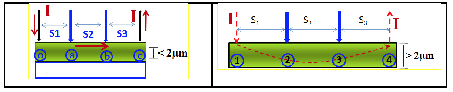
New Bi2Se3/BiOCl composites were synthesized with a p-n heterojunction by two different synthesis methods: coprecipitation and hydrothermal. Likewise, some synthesis parameters were modified such as the chelating agent concentration (EDTA) and the synthesis temperature. The materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectroscopy and XPS spectroscopy. The electrical conductivity of the materials was determined by measuring the resistivity using the four point probe method. The results show that different growth mechanisms of the species are generated in the different Bi2Se3/BiOCl composites, modifying the synthesis conditions. The morphologies and phases that are formed generate different electrical properties in these composites and the increase in the electrical conductivity of some samples can be attributed mainly to the formation of the stable p-n heterojunction between Bi2Se3 and BiOCl due to the generation of internal electric fields.
Keywords: Bi2Se3/BiOCl composites, Topological insulators, p-n heterojunctions, Electrical conductivity.
|
|
 |

