Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 18, No. 3 (2019), Poli367
Rheological behavior of plasma polymerized iodine-doped polypyrrole particles suspended in solutions of bovine serum albumin
|
O. Fabela-Sánchez, L. Medina-Torres, J. Morales-Corona, R. Mondragón-Lozano, A. Díaz- Ruíz, H. Salgado-Ceballos, M.G. Olayo, G.J. Cruz, C. Ríos, R. Olayo
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Poli367
Abstract
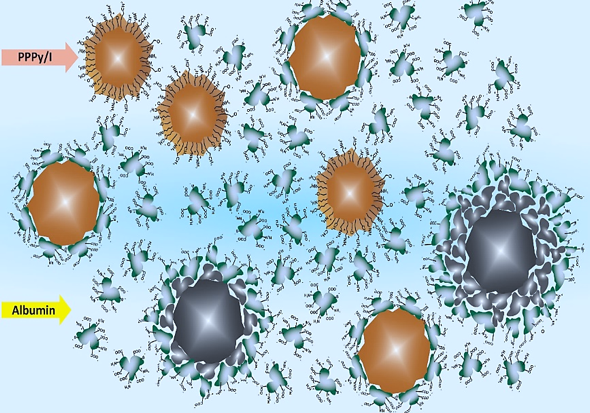 |
|
Multiple studies have demonstrated the great potential of polymers derived from pyrrole (PPy) as biomaterials in the health area. Iodine doped polypyrrole synthesized by plasma (PPPy/I) has shown good in vitroresults in cultures of various cell types as well as for treating traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) in laboratory animals.The objective of this study is to characterize the interactions between two agents that are potentially useful for repairing tissue, PPPy/I and the protein albumin of bovine serum (BSA); these materials and protein are known to behave separately, and they have not been used in combination as a treatment for TSCI. In this article, we present the rheological behavior of PPPy/I particulate suspensions in BSA solutions as well as the superficial physicochemical characterization of PPPy/I by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Contact Angle analysis (CA). The results show the changes that occur in the surface chemistry of PPPy/I due to its interaction with BSA and how these interactions generate a complex system in suspension. The shear rate-dependent viscosity changes in the suspension provide the combination of PPPy/I-BSA features that are ideal for a combined treatment via injection.
Keywords: Polypyrrole, Albumin, Rheometry, Spinal Cord Injury.
|
|
 |

