 |
|
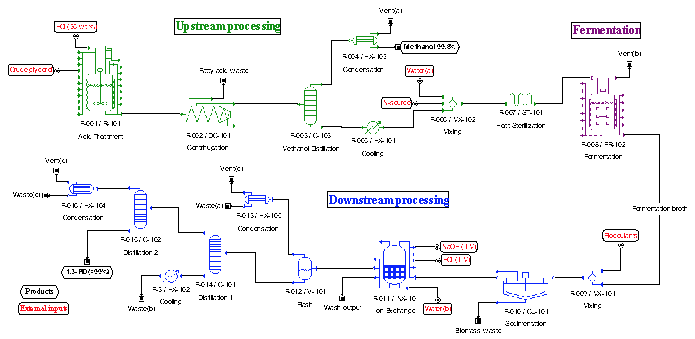
Crude glycerol is the major byproduct of the biodiesel industry, and its low price due to its abundant market supply impacts negatively on this industry. The microbial production of 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PD) is a very promising way for valorizing glycerol. Clostridium diolis DSM 15410 converts glycerol into 1,3-PD and is of industrial value due to its high fermentation yields and productivities. The aim of this study was to design a biotechnological process for the continuous production of 1,3-PD (> 99.0% purity) from crude glycerol using C. diolis DSM 15410 as biological system, and evaluate the process economic profitability under different scenarios. Optimal fermentation parameters were considered for the analysis. The effects of the selling price of 1,3-PD ($2.3-$6/t), the purchase cost of crude glycerol ($100-$300/t) and the process throughput (100-1,000 kg 1,3-PD/h) on the process profitability were studied. The results showed that process is economically profitable over a wide range of scenario combinations. This paper serves as a means for strategic decision making (e.g., go/no-go investment decisions) and further optimization of the 1,3-PD production process from crude glycerol.
Keywords: 1,3-propanediol, glycerol, modelling, simulation, economic analysis.
|
|
 |

