 |
|
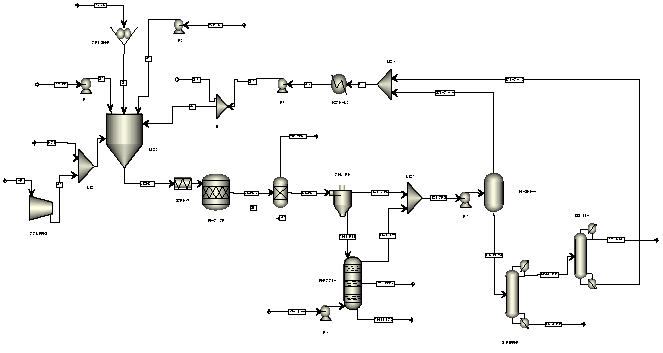
As one of the main agricultural producers in Latin America, Colombia generates important amounts of biomass residues that are currently discarded or incorporated into composting processes. Here, we propose a new process for the transformation of these residues into cellulose, which can be potentially used as a source for the manufacture of high-added value products. The process was designed and simulated in ASPEN PLUS where the 1-ethyl-3methylimidazolium acetate (EmimAoC) ionic liquid was used as solvent medium for the delignification of the biomass within the cellulose extraction process. The sustainability potential of the newly designed process was estimated by implementing the approach developed by Fan and Zhang (2012a), which allowed us to demonstrate higher profitability, lower energy consumption and environmental impacts, when compared with the Acetosolv process. Here, we selected this process for benchmarking purposes due to lower environmental impacts with respect to the well-established Organosolv and Kraft processes.
Keywords: simulation, ionic liquid, cellulose, sustainable, Acetosolv.
|
|
 |

