 |
|
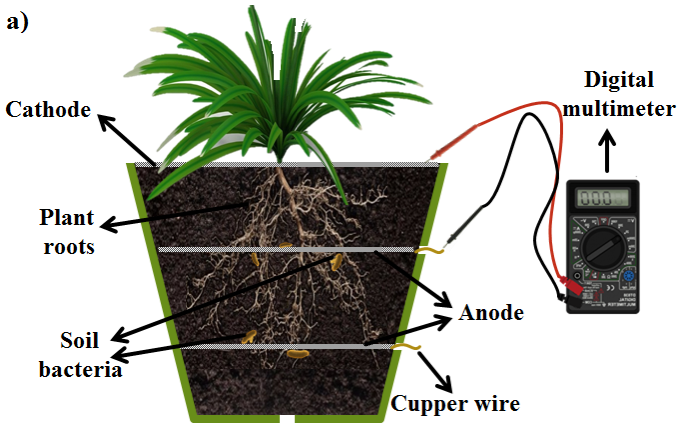
Due to the existing energetic demand worldwide the search for alternative energy sources is necessary. Bioenergy has been studied in the last decades as a promising energy source and the use of bioelectrochemical devices has become important. In this paper the plant Agapanthus africanus L. Hoffman’s was used to evaluate both growing and voltage generation in an electrochemical device adapted at the root system of the plant. For this, Agapanthus was planted either with or without compost and varying the position of the anode. Growth and voltage generation was monitored throughout all the experiments. All plants showed a satisfactory growth, and the carbon fiber anode position affect neither the vitality of the plant nor the system performance, moreover, the addition of compost (33%v) increased the generated voltage reaching a maximum value of 690 mV. Experimental data indicate a great potential of Agapanthus africanus to generate voltage in a green and sustainable way. Energy obtained from plant-microbial fuel cell can be used to power on low consumption electronics using an electronic device composed by 1.2 V batteries.
Keywords: Bioenergy, Bioelectrochemistry, Carbon fiber, Plant fuel cell, rhizomes.
|
|
 |

