 |
|
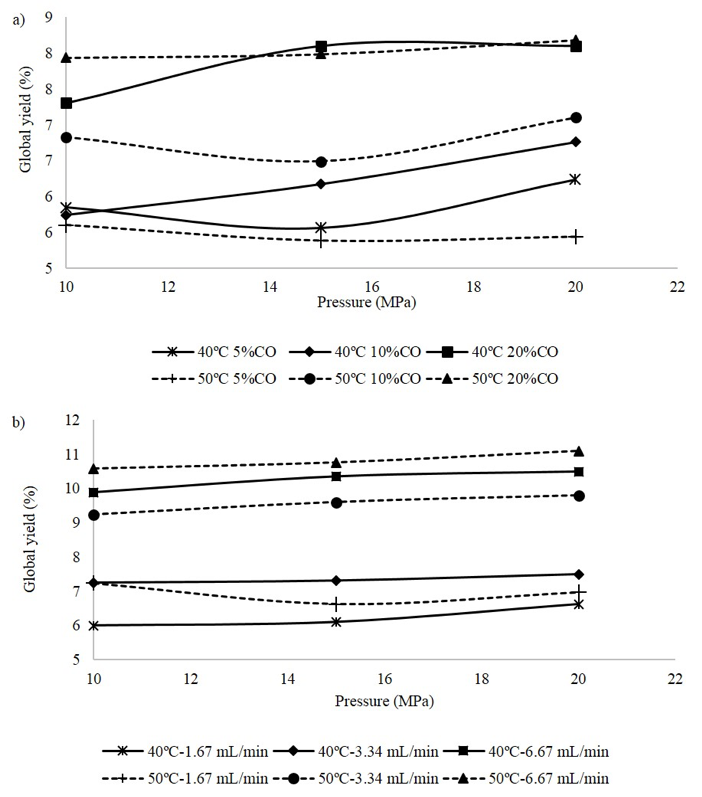
Currently, large quantities of by-products of mango are generated due to the high consumption of this fruit worldwide. In order to give it an added value, two "clean" technologies: supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) and pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) were evaluated for obtaining their analytes. Results indicated that although higher yields were obtained by PLE, in general a higher concentration of compounds (gallotannins, flavonoids, xanthones, gallic acid, etc.) was obtained by SFE, except for Gallic acid due to its high solubility in pressurized water. The best results for SFE were obtained at 50 °C, 20 MPa and co-solvent flow rate corresponding to 20 % of the CO2 flow; while for PLE the best condition was at 6.67 g.min-1 Milli-Q water, 40 °C and 10 MPa. This work provides additional information on the phytochemical composition of Brazilian Tommy Atkins mango peel and its possible use as a functional ingredient.
Keywords: bioactive compounds, by-product, extraction, mango, Tommy Atkins.
|
|
 |

