 |
|
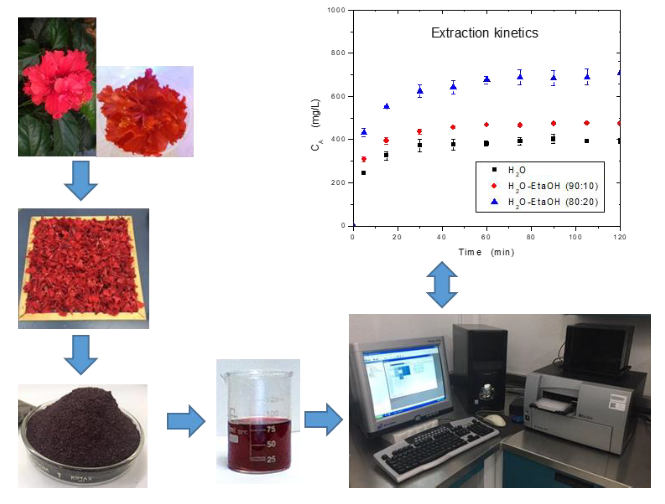
In this study the effect of temperature (25, 40 and 60 °C), solvent polarity using water (H2O)-ethanol (EtaOH) solvent with 100, 90:10 and 80:20 (H2O:EtaOH % v/v), and solvent-to-solid ratio (40/1, 60/1 and 80/1 mL/g) on the extraction yield of anthocyanins from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis was analyzed. The experimental data were fitted to Spiro and Siddique model with a good accuracy and the specific extraction rate constant was perfectly related to the apparent diffusivity using the lumped parameter model. The major percentage of the anthocyanin extraction yield was 63.81±1.33, 68.95 ±1.53, and 83.09±3.14 when the used solvent was H2O, H2O-EtaOH (90:10), and H2O-EtaOH (80:20), respectively. The diffusivity was affected mainly by temperature, tending to be more temperature sensitive as the solvent polarity decreased. Activation energy values, in range from 19.64 to 29.28 kJ mol-1, allow to infer that the extraction of anthocyanins is favored when using an ethanolic aqueous solution as a solvent. Response surface methodology was successfully applied to the anthocyanin extraction yield, confirming that the process parameters (solvent polarity, solid-to-solvent ratio and temperature) affected the extraction yields.
Keywords: Extraction kinetics, diffusivity, anthocyanins, Hibiscus rosa-sinensis.
|
|
 |

