Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 19, No. 2 (2020), Alim859
α-Zein nanoparticles as delivery systems for hydrophobic compounds: Effect of assembly parameters
|
C. Sánchez-Juárez, D. Reyes-Duarte, M. Hernández-Guerrero, M. Morales-Ibarría, J. Campos-Terán, I. J. Arroyo-Maya
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Alim859
Abstract
 |
|
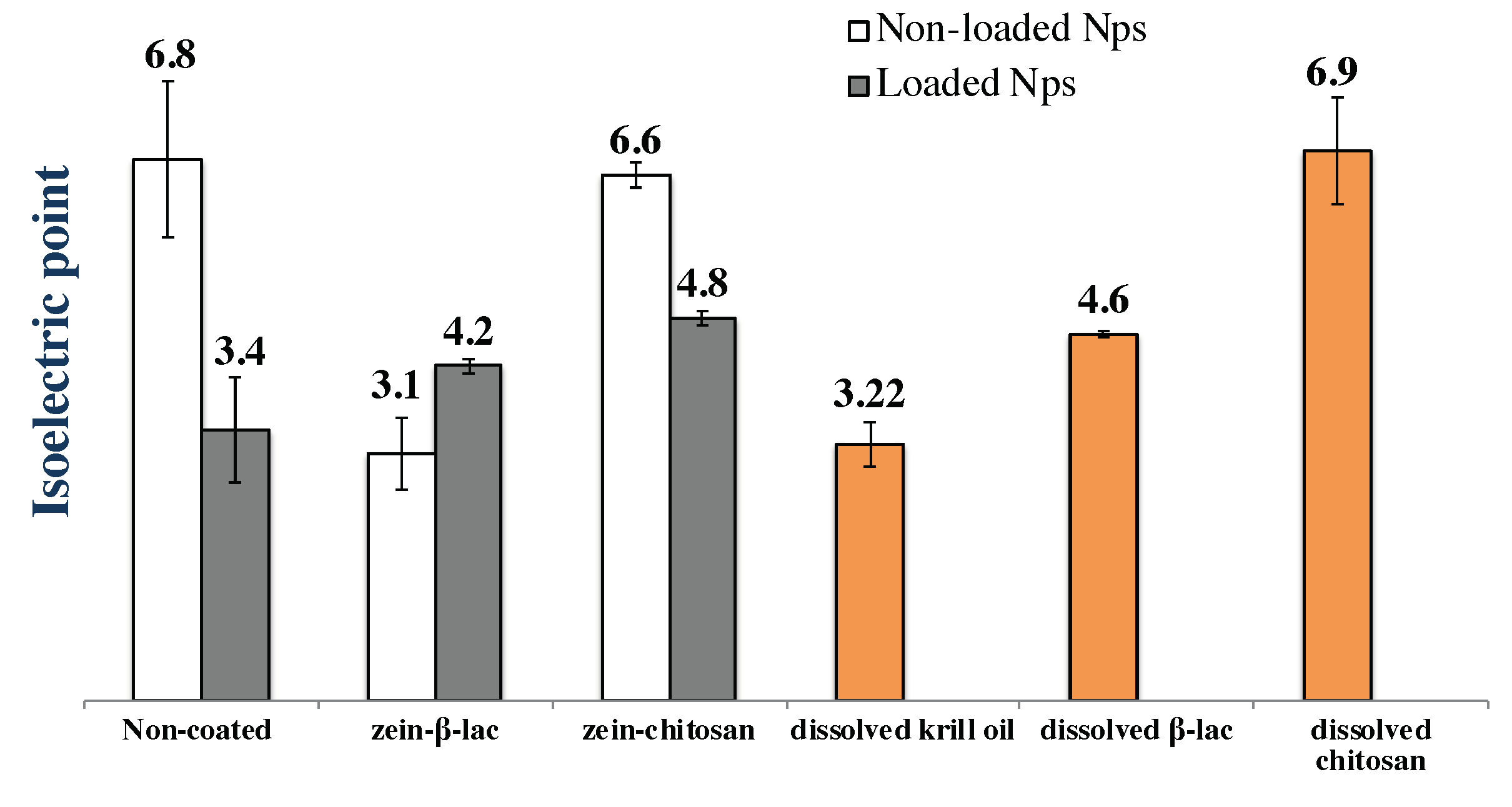
In this study, protein nanoparticles were assembled from a-zein using liquid antisolvent-precipitation methodology. The nanoparticles were loaded with krill oil, which is an important nutraceutical. The nanoparticles displayed different physicochemical characteristics depending on the assembly parameters chosen during their preparation. The fabrication process involved the use of biopolymer coatings (the protein b-lactoglobulin and the carbohydrate chitosan). Non-coated nanoparticles showed a particle size between 340-400 nm and surface charge of around -40 mV (pH 8.0). The protein copolymer b-lactoglobulin allowed the fabrication of smaller (d » 200 nm; z-potential » -60 mV) and more stable nanoparticles against pH changes (from 3.0 to 7.0). Chitosan was the best biopolymer coating for improving the antioxidant activity of the particles. The apparent pI for the different nanoparticles was modified after krill oil nanoencapsulation. These results support the idea that controlling the solvent system is a means to control physicochemical characteristics of a-zein nanoparticles.
Keywords: α-zein, krill oil, astaxanthin, biopolymeric nanoparticles, hydrophobic interactions.
|
|
 |

