 |
|
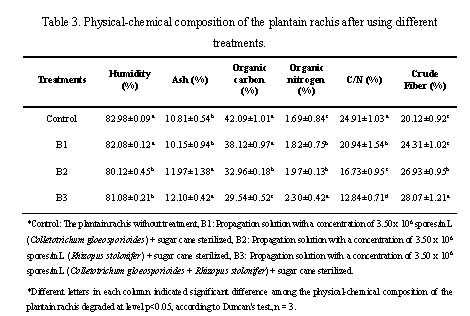
The phytopathogenic fungi such as: Colletotrichum sp. and Rhizopus sp. were isolated of banana and tomatoes respectively, 3 biodegradators were used: with spores Colletotrichum sp. (B1), with spores Rhizopus sp. (B2) and a mixture of spores Colletotrichum sp. + Rhizopus sp. (B3). Using the biodegradator (B3) was obtained the highest degradation of the plantain rachis being of 42.91%, and the leachates production was of 80 mL with pH of 7.96 on the 30th day of the experimentation. The banana rachis degraded by the mixture of spores of Colletotrichum sp. + Rhizopus sp. (B3) showed the lowest organic carbon content being of 29.52% and the highest nitrogen content being of 2.30%, generating a Carbon/Nitrogen (C/N) ratio of 12.84%. The results evidenced that the biodegradator composed by the mixture of Colletotrichum sp. + Rhizopus sp. (B3) can be used to increase the degradation of the plantain rachis encouraging the use of this biomass in the composting process.
Keywords: Biodegradator, Colletotrichum, phytopathogenic fungi, rachis, Rhizopus.
|
|
 |

