 |
|
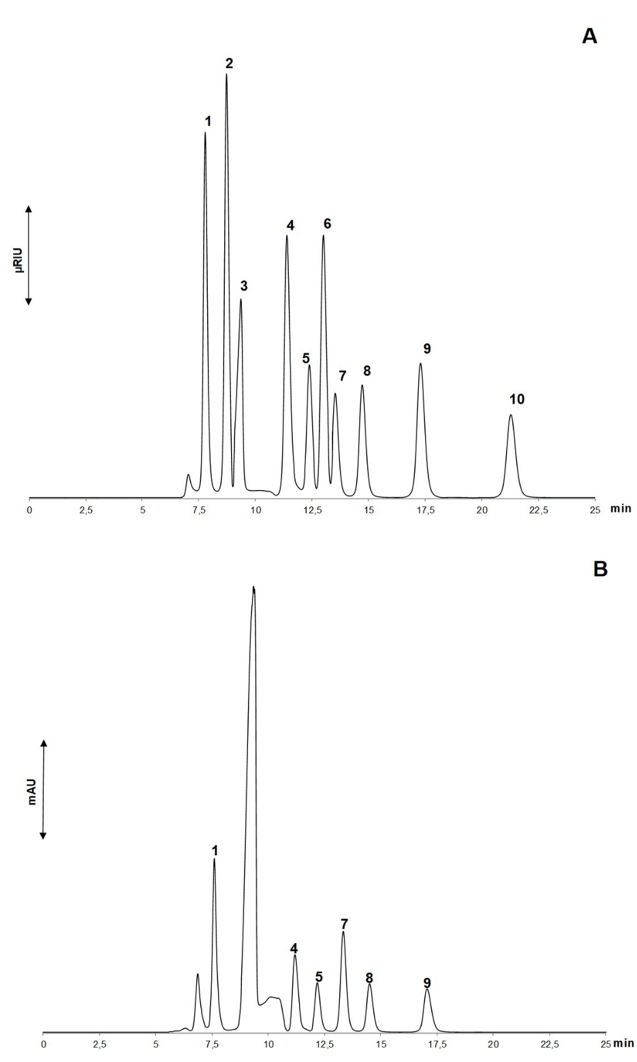
Bio-succinic acid process involves complex biochemical pathways in which diverse metabolites may be cogenerated. Their identification and quantification allow an adequate monitoring and understanding of the bioprocess. In this work, a HPLC methodology for simultaneous determination of glucose, glycerol, ethanol and citric, pyruvic, succinic, lactic, formic, acetic and propionic acids was validated, presenting adequate selectivity and linearity. Matrix effect was observed for citric and lactic acids, glycerol and ethanol. The limits of detection and quantification ranged from 0.006 to 0.021 g.L-1 and 0.018 to 0.065 g.L-1, respectively. Recovery values were between 89 and 109% and variation coefficients were less than 2.3%. The intermediate precision was verified with short-term stability, after one freezing and thawing cycle and analysis by a second analyst. The analysis of fermentation samples showed that Actinobacillus succinogenes’s metabolism was carbon source dependent, while Basfia succiniciproducens presented similar metabolic behavior for the carbon sources evaluated, with less variety of generated products. Succinic acid represented around 37% and 25% of products originated by fermentation of glucose and glycerol sources, respectively, using A. succinogenes. Meanwhile, maximum succinic acid production was equivalent to 50% and 80% of metabolites produced in the fermentation of glucose and glycerol sources by B. succiniciproducens.
Keywords: validation of analytical methodology, high added-value product, anaerobic fermentation, Actinobacillus succinogenes, Basfia succiniciproducens.
|
|
 |

