 |
|
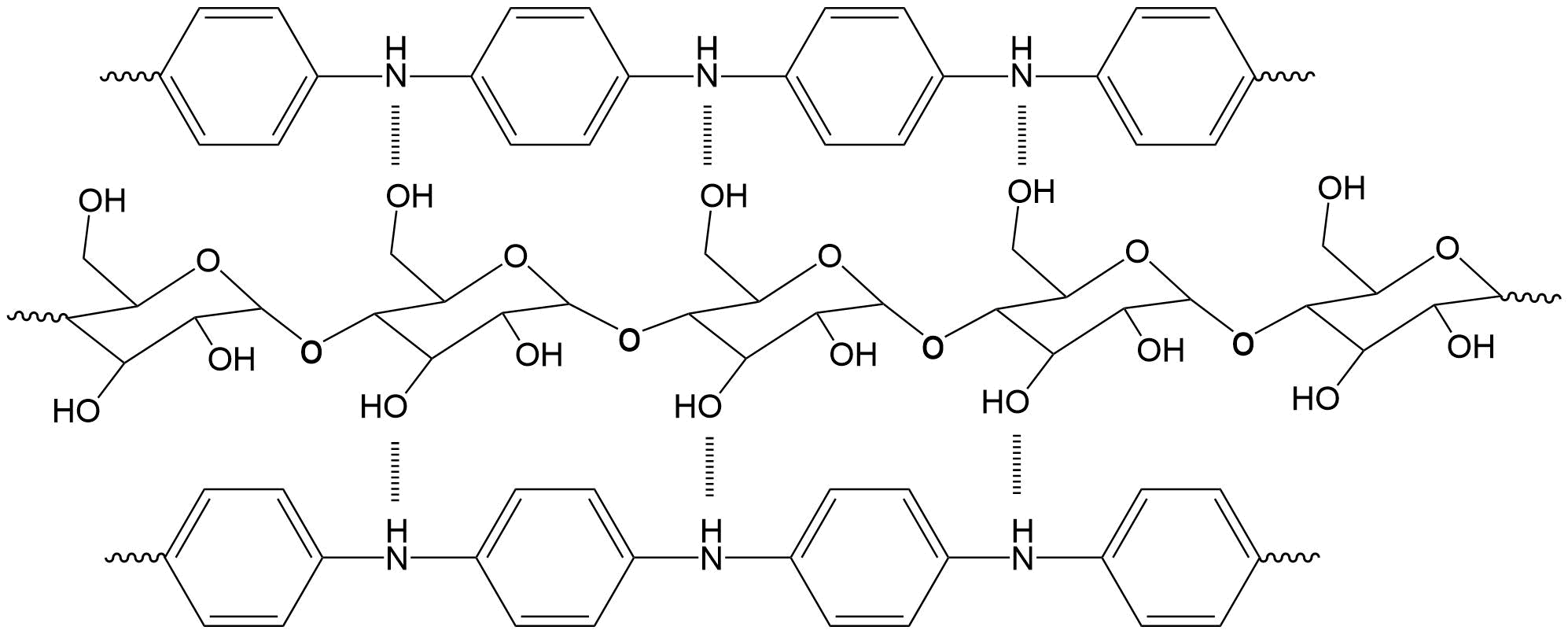
This paper presents the preparation of a composite material synthesized from a conducting biopolymer of cassava starch and polyaniline. The composite material was made from the addition of aniline to the synthetic mixture of a conducting biopolymer of cassava starch with plasticizers (glycerol, glutaraldehyde and polyethylene glycol) and lithium perchlorate. The resulting composite material was a dark colored film with flexible and stable consistency. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy showed that there is a possible interaction by hydrogen bonds between the structures of the origin polymers, established between the OH groups of the starch and the NH group of the polyaniline. On the other hand, the electrochemical response of the composite material presented redox activity, with oxidation and reduction process well marked and intense in its signals. Additionally, the electrochemical signals of the composite material were stable when recording 50 consecutive cycles.
Keywords: Solid biopolymer electrolyte, cassava, starch, polyaniline, composite material.
|
|
 |

