 |
|
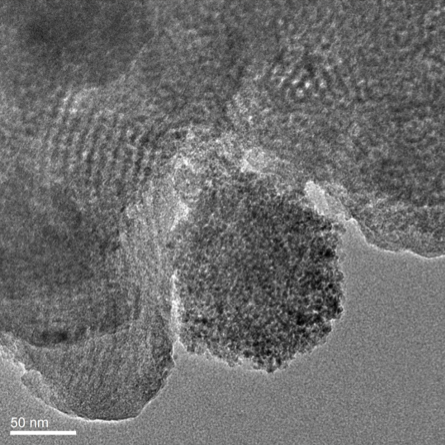
Pt (1 and 1.5 wt%) was impregnated on SBA-15 and corresponding Ti-modified composites at different TiO2 contents (3, 5, 10 and 20 wt%). Materials were characterized by N2 physisorption, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. SBA-15 had surface area greater than 800 m²/g that progressively decreased with increasing TiO2 content in binary materials. Very different hydrolysis rate of Ti and Si alkoxides could provoke encapsulation of segregated titania domains in SBA-15 structure. Highly reactive titanium butoxide hydrolysis-condensation could take place before reactions corresponding to tetraethyl orthosilicate. Pt dispersion clearly augmented with Ti concentration in composites where numerous tiny noble metal particles were observed on titania domains surface. Also, corresponding pore size maxima shifted to lower diameters (as to that of non-impregnated supports) after platinum loading suggested metallic crystals inside pores of Ti-modified carriers. However, some large cubic platinum crystals were also observed suggesting sintering (during calcining at 500 °C) of metallic particles weakly interacting with SBA-15 component. After materials annealing under air metallic platinum was evidenced (by XRD) pointing out to noble metal reduction during decomposition of organics from Ti and Si alkoxides used during carriers synthesis which presence was ascertained by FTIR.
Keywords: SBA-15, TiO2, platinum, composites, dispersion.
|
|
 |

