 |
|
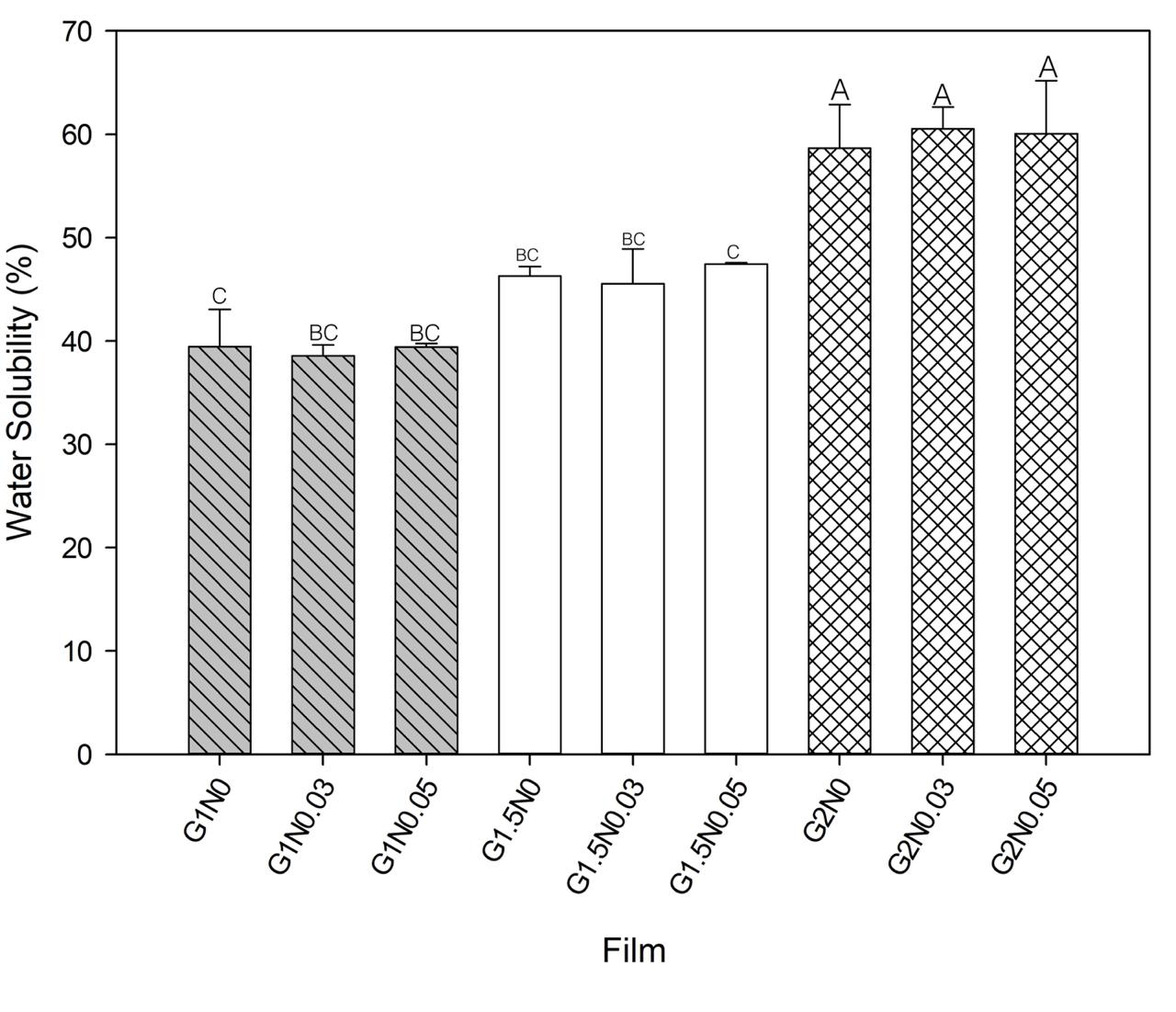
The films can be obtained from renewable resources such as polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids. Potato starch is a polysaccharide found in abundance, low cost, biodegradable, edible, and can be obtained from agro-industrial waste. In the present study, biodegradable films were obtained from potato starch mixed with montmorillonite nanoclay (MMT) as crosslinking agent and glycerin as a plasticizer; and thus characterize properties such as: permeability to water vapor, solubility, thickness, functional groups by FTIR, analysis of the morphology by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and mechanical properties. 9 mixtures combining different proportions of glycerol (1, 1.5 and 2 ml) with montmorillonite nanoclay (MMT) (0, 0.03 and 0.05 g) were prepared.
Keywords: potato starch, nanoclay, glycerol, biofilm, mechanical properties.
|
|
 |

