 |
|
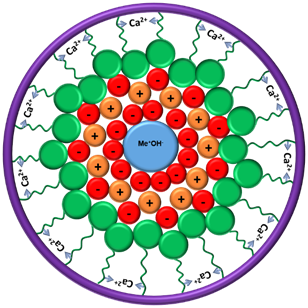
Groundwater samples from a mining community north of Mexico were studied, concentration of metals above the maximum allowable concentration from Mexican regulation were found. Spherical agglomeration technique (SAT) was used to remove metals (Pb, Cu, Cr, Ni, Zn, Mn, Cd). Two precipitating agents were tested: NaOH and Ca(OH)2. Also, Agave tequilana Weber extract as hydrophobicizing agent was employed to avoid metal redisolution. High metal removal proved the effectiveness on SAT application under a pH ranging between 9 and 11 and extract doses from 0.3 g extract/g pollutant. Better removal percentages were reached when using Ca(OH)2 as precipitating. Reported removal efficiency in that case yielded removal percentages as high as 99% removal for Pb under the three pH tested. The heavy metal evaluation index before treatment was 2354.91, but decreased to levels as low as 4.7 after SAT application.
Keywords: metal redisolution, hydrophobicizing agent, precipitation, spherical agglomeration technique, heavy metal evaluation index.
|
|
 |

