 |
|
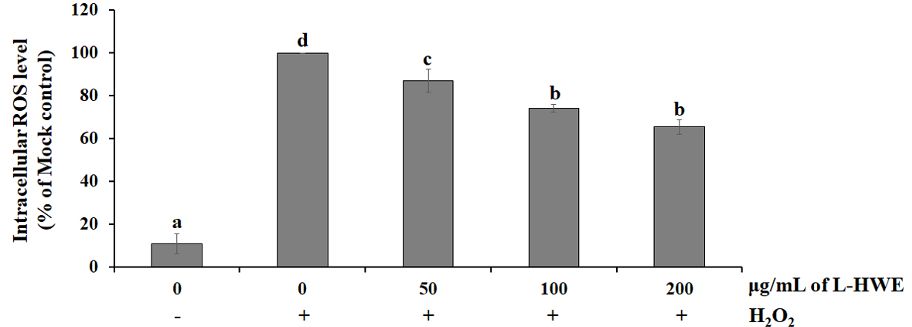
Petasites japonicus, a perennial flowering plant belonging to the Asteraceae family, has long been used in traditional herbal medicine for treating various diseases. The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of extraction methods including microwave-assisted extraction, autoclave-assisted extraction, and hot water extraction on the polyphenolic composition, antioxidant activity, and anti-melanogenic activity of P. japonicus leaves, stems, and roots. In comparison with other samples, leaf extracts exhibited strong DPPH radical scavenging activity, reducing power activity, and hydrophilic oxygen radical scavenging activity. In addition, the leaf extracts significantly suppressed α-MSH-induced melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells. Quantitative real-time PCR, western blot, and cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) analyses indicated that the anti-melanogenic effect of leaf extracts obtained by hot water extraction may result from the inhibition of ROS generation and the downregulation of tyrosinase expression in B16F10 cells. Furthermore, the extraction methods differentially affected the content of polyphenolic compounds and bioavailability of P. japonicus extracts. Taken together, the antioxidant activity and anti-melanogenic effect of leaf hot water extracts suggest that the leaves of P. japonicus could be a beneficial source of natural antioxidants for skincare products.
Keywords: Anti-melanogenic activity, Antioxidant activity, Petasites japonicus, Polyphenolic compounds.
|
|
 |

