 |
|
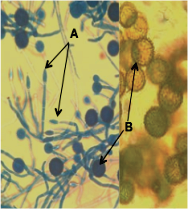
In this study, a Hypomyces chrysospermus ACL-01 fungus was isolated from the fruiting body of edible basidiomycete Boletus edulis, collected in Acaxochitlán in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico popularly known as tlacoayel. The effect of the isolated fungus against different fungal cereal pathogens was evaluated. The dual confrontation test and scanning electron microscopy analysis revealed that this ascomycete grows on the basidiomycetes Sporisorium reilianum and Tilletia sp., causing loss of cell viability. However, for the ascomycetes Bipolaris sorokiniana and Pyrenophora teres f. teres no effect was observed. On other hand Stenocarpella maydis and Fusarium sp. inhibited the development of H. chrysospermus ACL-01. The isolated strain produced extracellular enzymatic activities of the acid and basic proteases, chitinase and laccase. Cellulase and lipase activities were not found.
Keywords: Hypomyces chrysospermus, Boletus edulis, Tilletia sp., Sporisorium reilianum.
|
|
 |

