 |
|
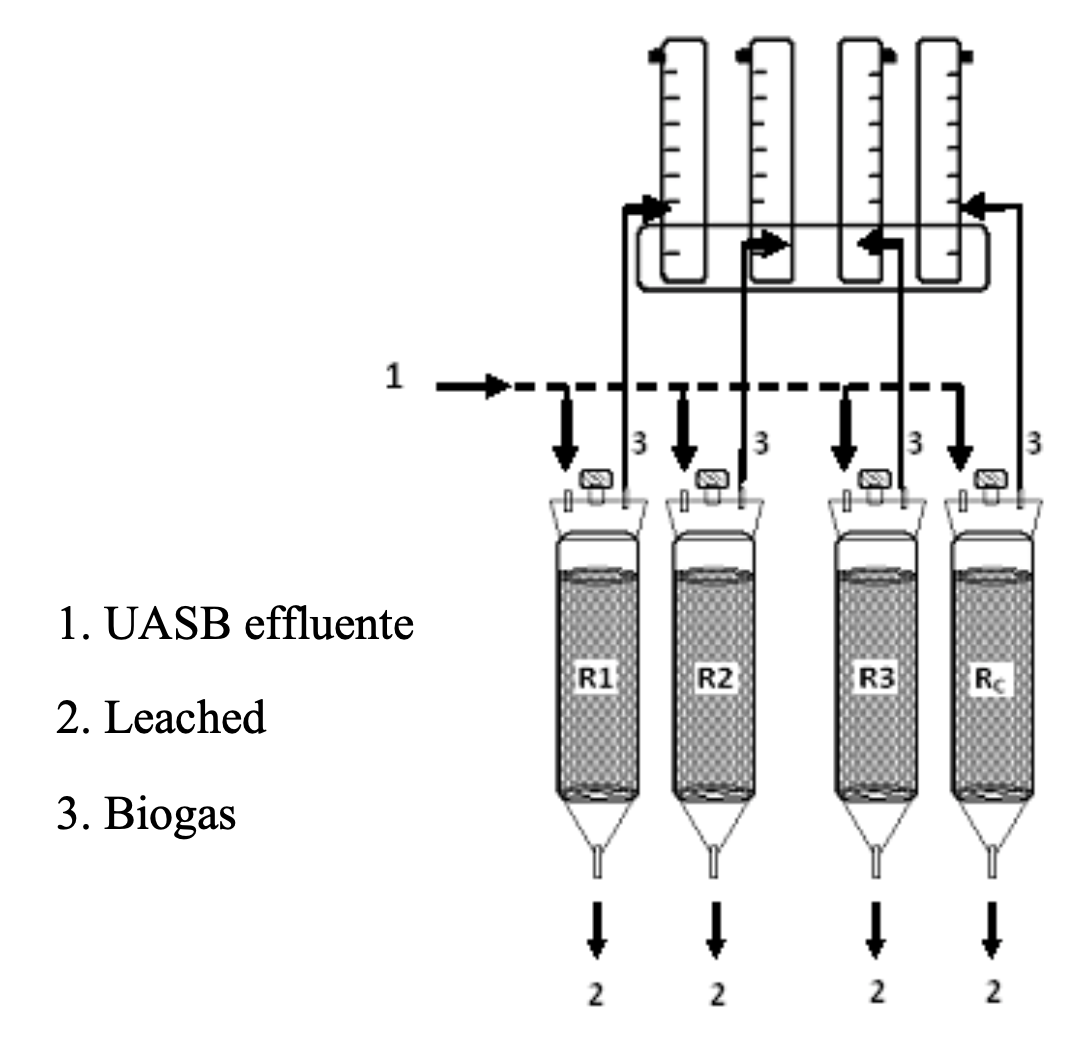
In the present work, the effect of an aerobic pretreatment on the hydrolysis and acidogenesis of the organic solid wastes (OSW) was evaluated. The aerobic pretreatment was carried out under three incubation conditions: the first condition was at 30°C for 24 hours (isothermal), the second condition was at 30°C for 12 hours followed by 12 hours at 35°C, and the third condition was at 35°C for 12 hours followed by 12 hours at 40°C. During the aerobic pretreatment, the enzymatic activity was analyzed and the product obtained from the pretreatment was subsequently fermented in anaerobic hydrolytic leach bed (AHLB) reactors to obtain volatile fatty acids (VFA). The best hydrolysis results were achieved with the aerobic pretreatment at 30°C for 24 hours, obtaining activities of xylanases and pectinases of 115 and 73 U g-1 dry matter (DM) respectively after 18 hours and 100 U g-1 DM of proteases at the beginning of the process; values that are 2.7, 2 and 4 times higher than previously report. Also, a hydrolysis constant (k) of 0.081 d-1 was obtained, with the productivity of VFA of 0.82gLr-1d-1, with predominance in acetate, the main precursor of methanogenesis in the final stage of anaerobic digestion.
Keywords: Organic Solid Wastes (OSW), aerobic pretreatment, hydrolysis, leachate, volatile fatty acids.
|
|
 |

