 |
|
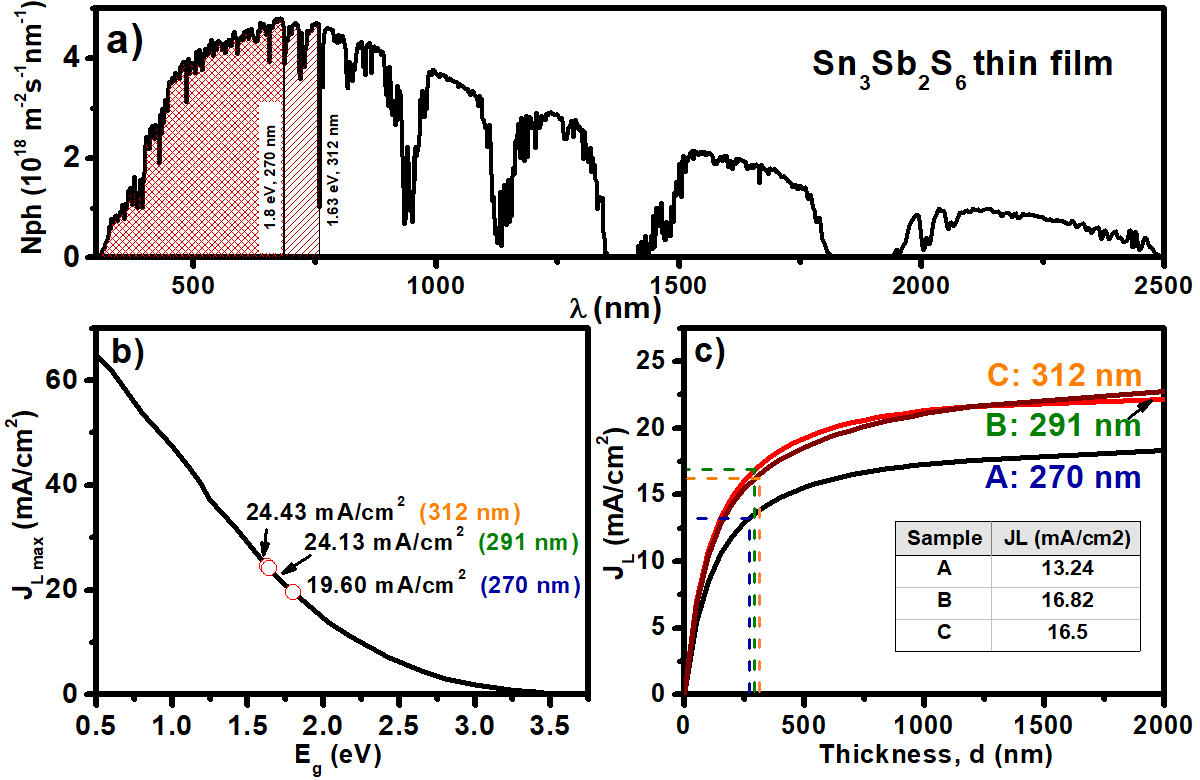
In this work, SnS-Sb2S3 stack films were formed by sequential chemical deposition, and then they were annealed in a nitrogen atmosphere to synthesize Sn3Sb2S6 thin films successfully. The structural and optical properties were studied by X-ray diffraction and transmittance and reflectance. All the samples show a high absorption coefficient of > 105 cm-1 in the visible region. Their optical bandgap and refractive index are between 1.6-1.8 eV and 3.00-2.71, respectively, which decrease with the increase of film thickness. The electrical conductivity is in the range of 10-8 to 10-7 Ω−1 cm−1. The light-generated current density (JL) is presented as a function of Sn3Sb2S6 film thickness when exposed to air mass 1.5 global (AM1.5G) and solar radiation intensity of 1000 W/m2. In short, Sn3Sb2S6 thin films obtained via the proposed new route exhibit appropriate properties for solar cell applications.
Keywords: sulfosalt thin films, chemical deposition, Sn3Sb2S6, thermal annealing process.
|
|
 |

