 |
|
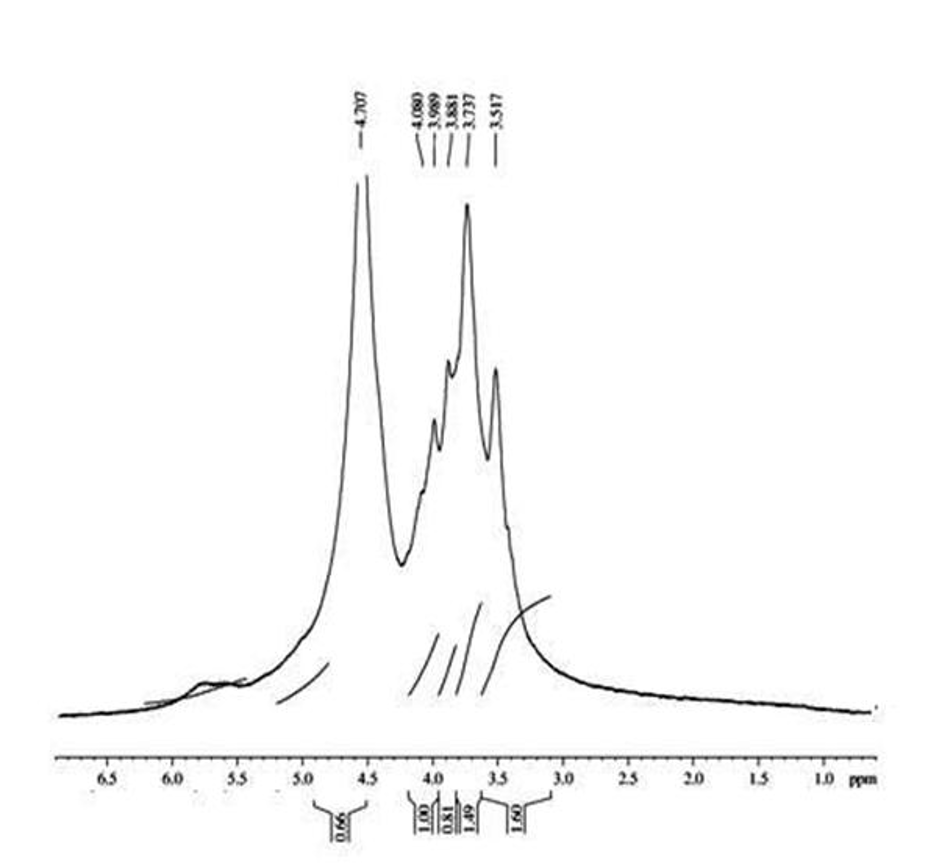
Current work was endeavoured to formulate the topical gels of 4 % lidocaine HCl by employing dillenia (Dillenia indica L.,) fruit gum (DG) extracted from ripen fruits (14.73% yield). Physicochemical properties such as colour, odour, taste, aqueous solubility, pH and viscosity of this extracted DG were evaluated. Occurrence of carbohydrates and mucilage was confirmed by phytochemical identification tests and was characterized by employing FTIR and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Employing extracted DG along with Carbopol 940 (as gel-forming materials), propylene glycol (as plasticizer), methyl paraben (as preservative) and menthol (as permeation enhancer), topical gels containing 4 % lidocaine HCl were formulated. The pH and viscosity of these gels were satisfactory. The ex vivo skin permeation of lidocaine HCl across excised porcine ear skin membrane from formulated and marketed topical gels containing 4 % lidocaine HCl exhibited sustained permeation over 7 h. Highest lidocaine HCl permeation flux (1589.66 ± 13.36 µg/cm2/h) was measured for the gel containing 0.1 % menthol. Korsmeyer-Peppas model was found as the best-fitting drug permeation model (R2 = 0.9944-0.9992) with super case-II transport mechanism (n = 0.97-1.07). These topical gels of lidocaine HCl (4 %) were found physically stable enough without syneresis in the freeze thaw cycling process.
Keywords: Dillenia fruit gum, topical gels, drug permeation, lidocaine HCl.
|
|
 |

