 |
|
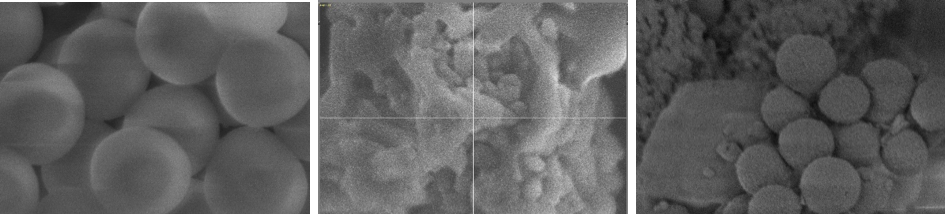
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), is a cationic surfactant used in synthesis of silica oxide spheres (SiO2), which can be used in biomedical applications, however, CTAB is cytotoxic and residues can be found within the SiO2 pores, therefore, the removal of CTAB, is crucial. In the present work, the preparation and purification of SiO2 is described. The effect of heat treatment against argon plasma treatment on SiO2 spheres and their efficiency in removing CTAB was analyzed. The plasma treatment was performed using argon, at 50, 100, 150 and 200 W of power, for 1 h, it was also performed at 200 W for 1.5 h. The techniques; DLS, FTIR-ATR, SEM, BET, were used for characterization, in addition to hemolysis studies. The results showed a decrease in surfactant at powers of 150 and 200 W and 1 h. The plasma treatment at 200 W and 1.5 h of treatment, according to the FTIR-ATR, caused a total removal of the surfactant and a 16% increase in the surface area according to the BET analysis, the plasma treatment turned out not to be hemolytic.
Keywords: Biomedical applications, Plasma treatment, Silica Oxide, Heat treatment.
|
|
 |

