 |
|
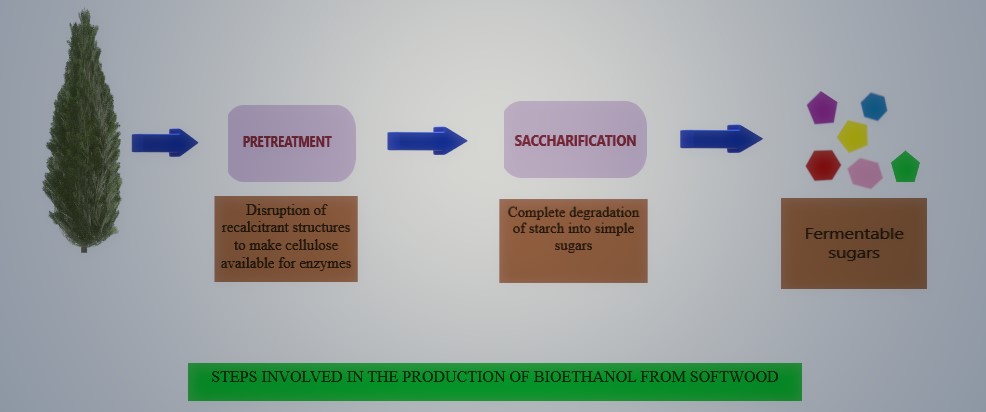
The present study focuses on the use of thermophilic recombinant cellulases to produce fermentable sugars for conversion to bioethanol which is an important renewable energy resource to be worked upon due to climatic change, energy insecurity and nonrenewable nature of fossil fuels. Therefore, sawdust of pinus wood was subjected to pretreatment using different acids such as phosphoric, nitric, acetic and alkalis i.e. sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide and ammonia in various concentrations. Maximum delignification was observed using 8% nitric acid as it resulted in to 74.02% delignification and increased the cellulose availability to 81.8%. Subsequently, pretreated biomass was assessed for improvement in hydrolysis to less complex sugars employing thermophilic recombinant cellulases cloned from Thermotoga petrophila. Saccharification reaction parameters such as Incubation time, temperature, biomass and enzyme concentrations were optimized. The optimized conditions were revealed as 3 h incubation time, 65℃ temperature 0.1 % (w/v) substrate, 250, 2550 and 70140 U of Endo-1,4-β-glucanase, Exo-1,4-β-glucanase and β-1,4-Glucosidase, respectively. This optimization study resulted in 34.61% saccharification yield which is 1.82 folds increase compared to saccharification yield of untreated biomass. This study is unique in providing insight to pretreatment using Nitric acid as in literature use of nitric acid as a pretreatment agent is not well investigated.
Keywords: Green energy, Renewable energy, Biofuel, Catalysis, Bioconversion.
|
|
 |

