 |
|
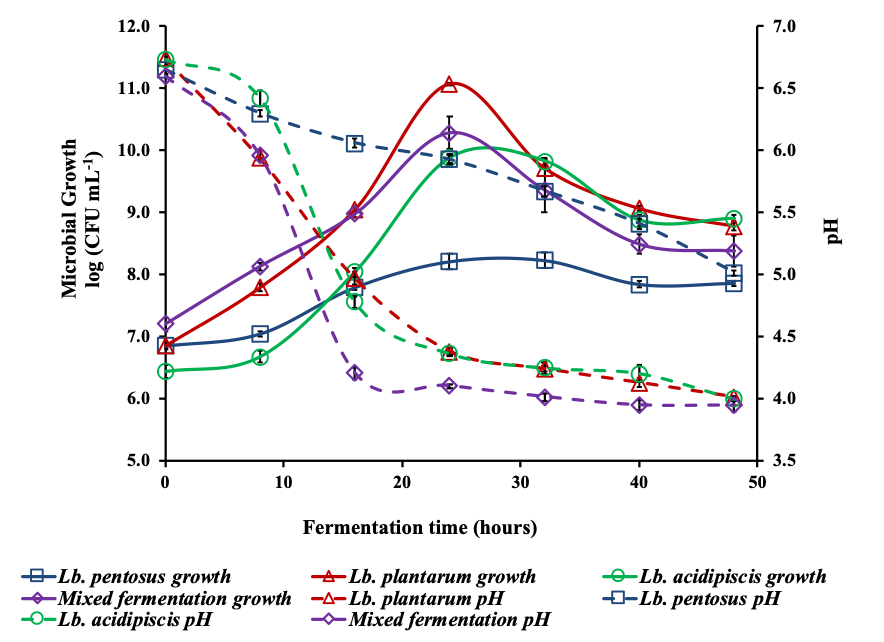
Some probiotic lactic acid bacteria could generate bioactive peptides during milk fermentation. The aim of this work was to evaluate the ACE inhibitory and mineral-binding (calcium and iron) activity during milk fermentation by three probiotic LAB strains (Lactobacillus plantarum, Lb. pentosus and Lb. acidipiscis) as well as mixed fermentation. These strains were previously isolated from Chiapas double cream cheese. The fermentation that showed the highest microbial growth was performed by Lb. plantarum, followed by mixed fermentation and Lb. acidipiscis. However, the mixed fermentation had higher proteolysis. Milk fermentations performed with Lb. acidispiscis, Lb. pentosus and mixed showed high ACE-inhibitory activity (97%). The Lb. plantarum and mixed fermentations showed the higher iron-binding activity, 99 % and 97, respectively, whereas the Lb. acidipiscis and mixed fermentations had the highest calcium-binding activity. These results showed that probiotic microorganisms isolated from double cream cheese have great potential to be used in the production of functional foods.
Keywords: Lactic acid bacteria, ACE-inhibitory activity, metal-binding activity, double cream cheese, halotolerant probiotics.
|
|
 |

