 |
|
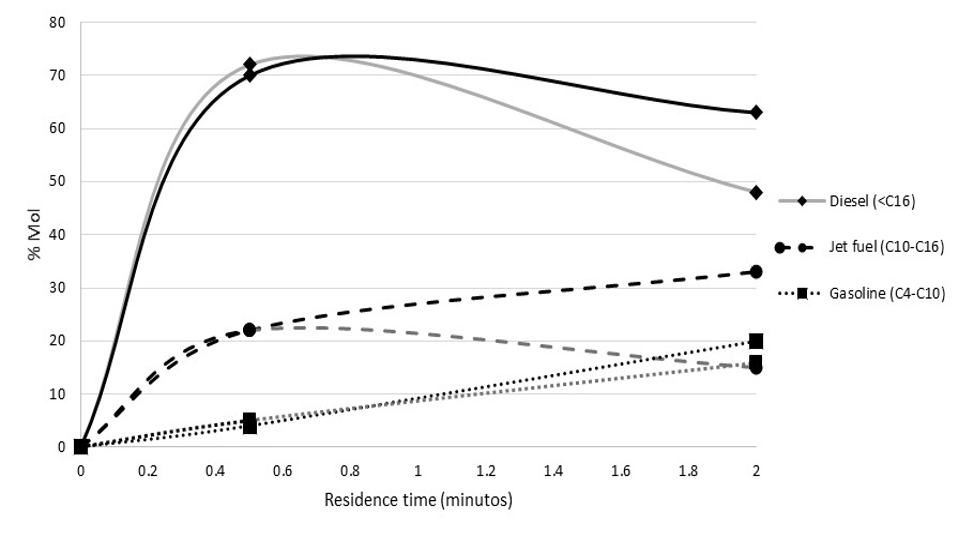
This work evaluated the activity of two commercial catalysts Ni-Mo/Al2O3 and Co-Mo/Al2O3 for the hydrodesulfurization process (HDS) developed by the Mexican Petroleum Institute (IMP). The process is performed on Jatropha curcas oil, due to its excellent flow properties at room temperature, allowing its mixing with commercial hydrocarbon cuts. Catalysts have the characteristic of the hydrodeoxygenation reactions of fatty acids present in J. curcas vegetable oil for the generation of chemically similar hydrocarbons to those of fossil origin.
The following conditions were evaluated: pressure of 145 -400 psia, temperature from 300 to 390 °C and residence times of 0.5 and 2.0 min (WHSH -60 h-1 and 30 h-1). HDS process activity with pure J. curcas oil and 20% mixture with n-hexadecano as a model molecule of HDS hydrocarbons. The Ni-Mo/Al2O3-type catalyst showed increased conversion of triglycerides and fatty acids to linear-chain hydrocarbons, being greater than 85%, compared to the Co-Mo/Al2O3-based catalyst, which had a conversion of close to 82%. Catalytic activity was also observed to be very temperature-dependent.
Keywords: Biofuels, Hydroconversion, Jatropha curcas, Bifunctional catalyst, Catalytic selectivity.
|
|
 |

