 |
|
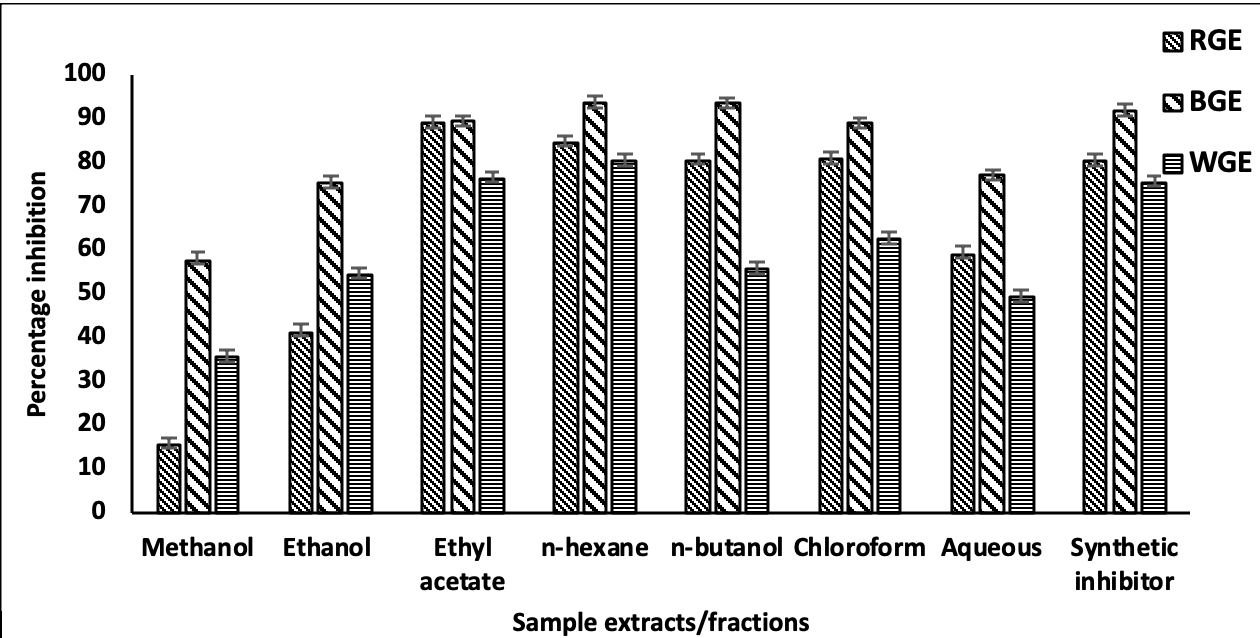
An organized biofunctional characterization of red, black, and white ginseng root extracts and fractions was performed. To assess antioxidant, antiglycation, enzyme inhibitory, antiamnestic, cytotoxic, thrombolytic, antibiofilm potentials in roots of three Panax ginseng preparations (red, black, white), powdered material was extracted and fractionated into different solvents. Antioxidant activity, phenolic and flavonoids contents were assessed by using free radical scavenging, Folin–Ciocalteu reagent and aluminum chloride colorimetric assays. Antiglycation and enzyme (alpha amylase, alpha glucosidase and acetylcholinesterse) inhibition activities were tested by prescribed methods along with cytotoxic (antihemolytic profile), thrombolytic activity, and biofilm growth inhibition assays. Red and black ginseng indicated maximum phenolic contents (37.26 ± 1.563 g GAE) and flavonoid contents (149.4 ± 2.032 g CE) respectively. The DPPH scavenging ability (62.84%) of red ginseng was higher than black and white ginseng. Significant antidiabetic activities were exhibited by black and white ginseng. The highest antihemolytic (71.2%) and thrombolytic (87%) actions were shown by black and red ginseng respectively. Red and white ginseng maximally inhibited the growth of Pasteurella multocida while in the case of Staphylococcus aureus, red ginseng showed optimum antibiofilm activity. The present study demonstrates that all three preparations of P. ginseng have effective yet variable functional characteristics that warrant further exploration.
Keywords: P. ginseng, antioxidant, enzyme inhibition, antidiabetic, phenols, biofilm.
|
|
 |

