 |
|
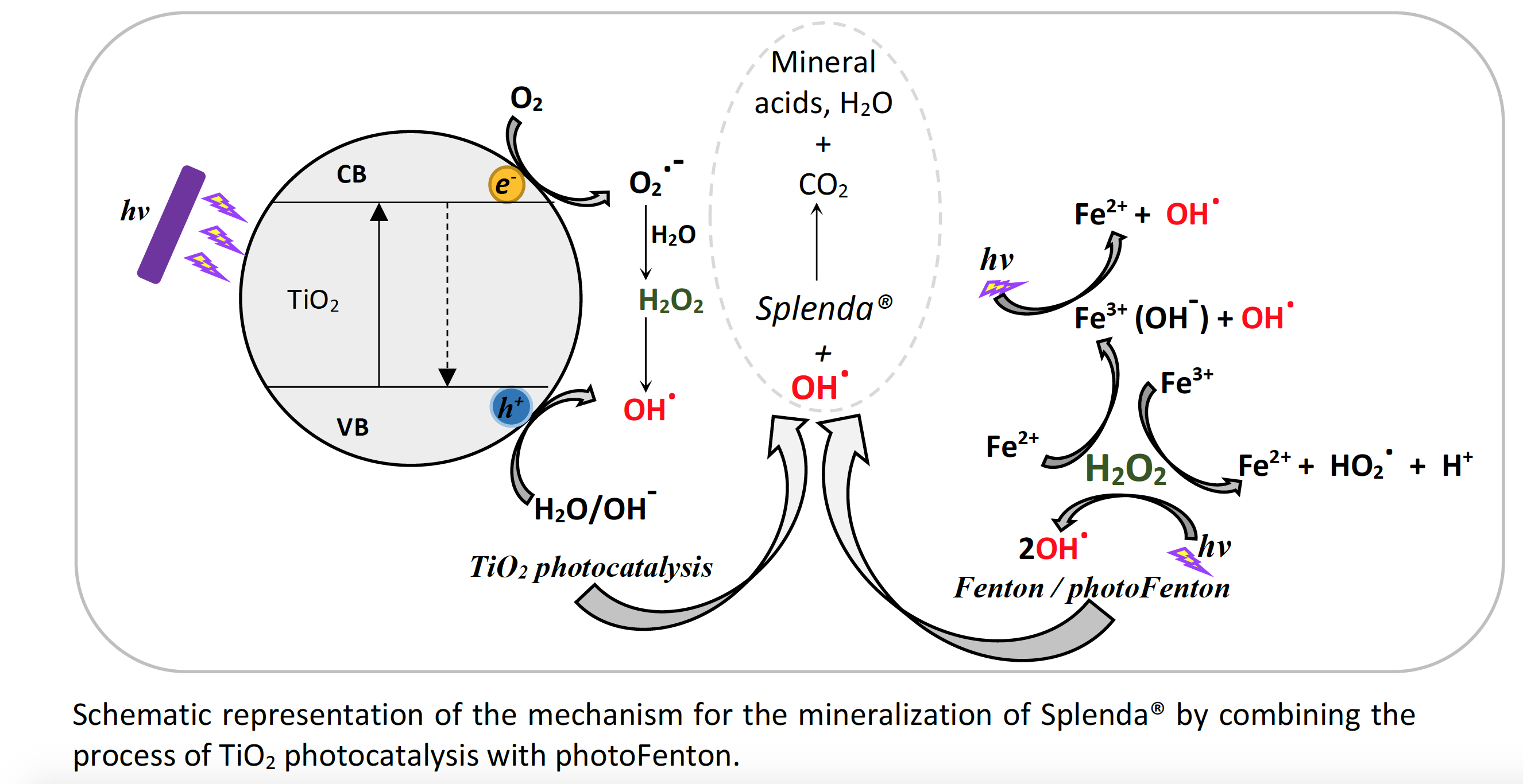
The pollutant legislation and its ecotoxicological dates recognize several water pollutants. However, there are others that have not yet been recognized as emerging organic pollutants because the damage that could be caused to the environment, especially in the water, is still unknown. For example, it is interesting to pay attention on Splenda because is increasingly consumed worldwide today. Splenda is one of the emerging pollutants that has not yet been formally declared as a pollutant, but there are some findings that show Splenda as a water pollutant, specifically the sucralose molecule, due to persistence in the environment. In this work, the mineralization of Splenda, in different initial concentrations (72 mg l-1, 144 mg l-1 and 288 mg l-1), was carried out by TiO2 photocatalysis assisted with photo-Fenton. Splenda mineralization is less than 58% by these processes when used separately; however, Splenda was mineralized 62.8% (72 mg l-1), 83.7% (144 mg l-1) and 58.8% (288 mg l-1) by TiO2 photocatalysis assisted with photo-Fenton at 2 h, 5 h and 5 h, respectively. In all cases, the mineralization followed a pseudo-first-order reaction.
Keywords: water, emerging contaminant, photo-Fenton, TiO2 photocatalysis, sucralose- Splenda®.
|
|
 |

