 |
|
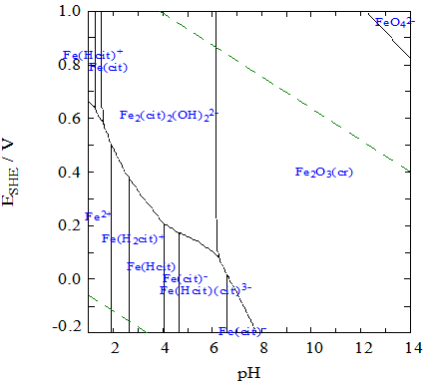
Recycling of industrial waste has become a process of highly positive impact on the environment, industry and human health. The management of the electric arc furnace dust (EAFD) is a necessary and interesting task due to the possible recovery of its elevated metallic content (Zn, Pb, Cu, etc.). This reduces the environmental pollution generated by the leachability of its heavy metals and produces new revenues for the steel industries. In this work, a hydrometallurgical route was studied to extract the zinc present in EAFD. The research carried out using two carboxylic acids: sodium citrate and oxalic acid at moderate concentrations (≤ 0.5 M). The effect of pH, molar concentration and stirring speed was analyzed. Under pressure and ambient temperature, after 3 h of leaching, the results showed that both agents can leach zinc from waste, reaching metal extractions of approximately 50%. The more stable franklinite (ZnFe2O4) and hematite (Fe2O3) phases were not decomposed under these mild conditions. Citrate was especially promising due to its selectivity for zinc.
Keywords: EAFD, leaching, sodium-citrate, oxalic-acid, zinc.
|
|
 |