Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 20, No. 2 (2021), Cat2346
Cost-effective functionalization of Vulcan XC-72 by using the intermittent microwave heating process as nanocatalyst support for ethanol electrooxidation in acid media
|
W.J. Pech-Rodríguez, F.J. Rodríguez-Varela, E. Rocha-Rangel, D. González-Quijano, J.C. Martínez-Loyola, G. Vargas-Gutiérrez, G. Suarez-Velazquez, C. Morais, T.W. Napporn
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Cat2346
Abstract
 |
|
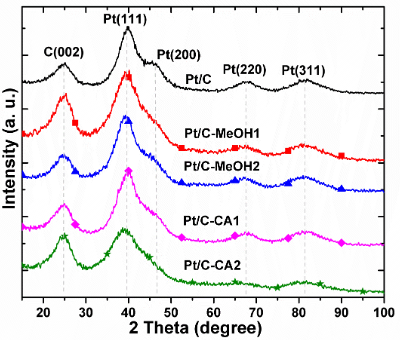
Vulcan XC-72 samples were functionalized with methanol (MeOH) by Intermittent Microwave Heating (IMH) under different treatment conditions. To assess the effectiveness of the proposed method citric acid functionalization was also performed as comparison. The obtained carbonaceous supports were used to synthesize the Pt/C-MeOH and Pt/C-CA nanocatalysts. The effectiveness of the surface treatment was assessed by using them as support for Pt/C nanocatalysts and conducting investigations towards the Ethanol Oxidation Reaction (EOR). The most active nanocatalyst was Pt/C-MeOH2 (0.15 mol L-1 MeOH and 8 min heating) which generated a current of 63.7 mA cm-2. In situ SPAIRS measurements showed that the EOR at Pt/C-MeOH2 and Pt/C-CA1 follows a C2-pathway mechanism. Meanwhile, a competition between the C1 and C2 pathway was observed at Pt/C. The study demonstrated that the IMH functionalization of Vulcan with MeOH produces carbon supported Pt nanocatalysts with enhanced catalytic activity for the EOR, with potential application in Direct Ethanol Fuel Cells
Keywords: Green Vulcan surface functionalization, microwave heating, Pt/C nanocatalysts, in situ SPAIRS analysis, Ethanol Oxidation Reaction.
|
|
 |

