 |
|
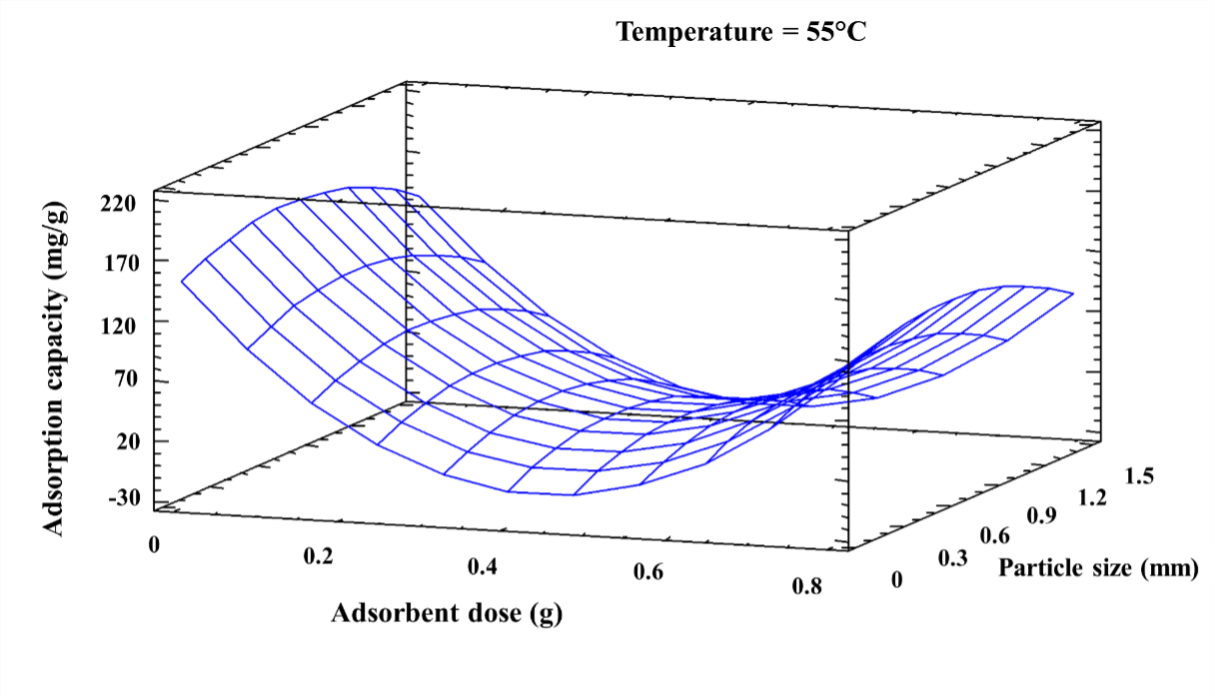
The objective of this work was to evaluate in a batch system the effect of temperature, adsorbent dose and particle size in the elimination of Cadmium (II) ions using corn cob (Zea mays). A central 22 star composite type experimental design was used. From the characterization of the bio-adsorbent by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), it was found that its structure has OH, COOH, methyl and amino groups, intervening in the process. It was found that at 55 ºC, 0.031 g and 0.6775 mm the maximum adsorption capacity was obtained (210.1 mg/g). From the kinetics, it was established that removal occurs rapidly in the first minutes and equilibrium is reached at 120 min, the data being adjusted by the Pseudo-Second order model. The adsorption equilibrium data is fitted by the Langmuir model, suggesting that it occurs uniformly on the surface of the bio-adsorbent. Corn cob is presented as an effective adsorbent for Cadmium (II) in aqueous solution.
Keywords: bio-adsorption, kinetics, isotherm, Langmuir, pseudo-second order.
|
|
 |

