 |
|
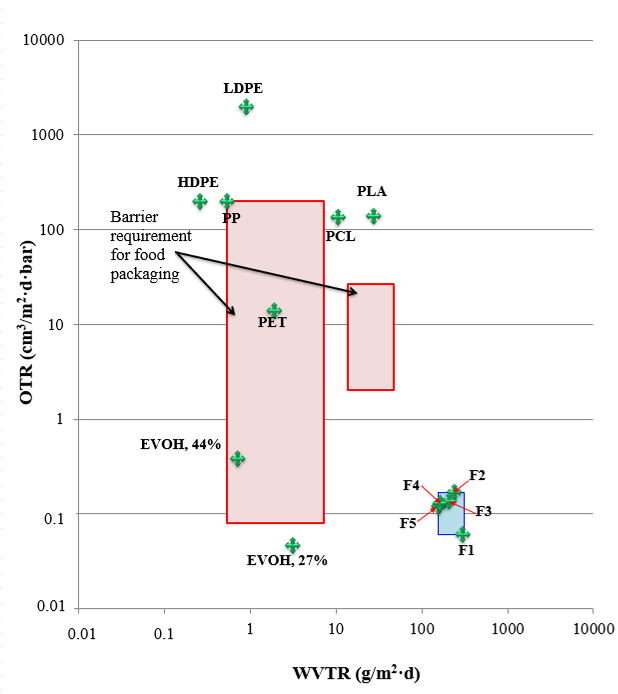
The present work aims to study the incorporation effect of montmorillonite and polycaprolactone clays to a matrix of thermoplastic cassava starch plasticized with glycerol, the blends were obtained by extrusion process and the films by compression molding. The physicochemical, mechanical, optical and barrier properties were characterized. The addition of polycaprolactone and montmorillonite reduced the water solubility of the films and improved and the water vapor transmission rate. The oxygen transmission rate of the formulations is lower than that of some conventional polymers and comparable with Ethylene-Vinyl-Alcohol (EVOH). The addition of montmorillonite produced more rigid and less deformable films, with low gloss and low internal transmittance at 650 nm. The materials obtained are friendly to the environment and have functional properties suitable for packaging foods with low humidity, such as bakery products or flours.
Keywords: Montmorillonite clays, thermoplastic starch, polycaprolactone, extrusion process.
|
|
 |

