 |
|
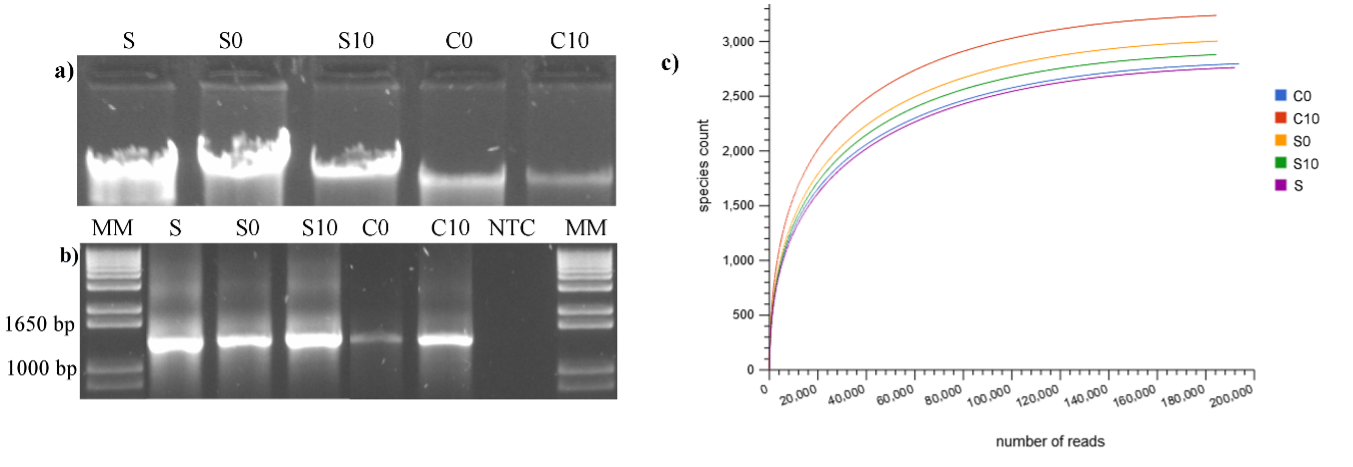
Recently, metagenomic DNA based analysis gained importance in fields such as environmental sciences and bioenergy, where mixed microbial communities embedded in complex matrixes, play a crucial role. Therefore, financially economical, and high quality metagenomic DNA extraction protocols are needed. In this work, a rapid and inexpensive method for high quality DNA extraction from a variety of complex samples was performed; the average DNA yield was 71.65 ng µL-1, with an average purity of 1.68 (A260/A280). The cost of extraction per sample was about 76 % less in comparison with commercial kits and the time needed to obtain the DNA pellets was about 4 hours. The DNA was suitable for 16S rRNA gene amplification by PCR and for next generation sequencing analysis, employing a MiSeq Ilumina platform. A high microbial diversity was detected in this study, and three main groups of bacteria were observed, which were developed according to the effect of the activated carbon had on them. The analysis performed showed a great difference between the samples, highlighting the differences between the microbial communities developed in the activated carbon biofilm and the bacteria detected in the reactor without activated carbon.
Keywords: Metagenomic DNA extraction, carbon biofilm, sludge sample, PCR based 16S rRNA analysis.
|
|
 |

