 |
|
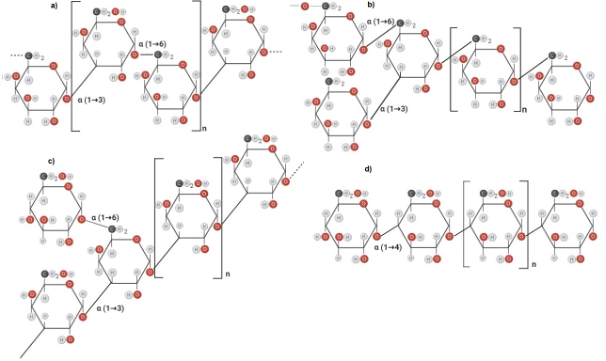
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are classified in two groups, homopolysaccharides (HoPs) and heteropolysaccharides (HePs), are produced by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and used in a range of industrial applications including the medical and food industries. HoPs are extracellular EPSs and their production depends on extracellular enzymes, while HePs are intracellular EPSs. Their nature (extra or intracellular) directly impacts production rates, HoPs having higher yields. The development of processes for producing EPSs has attracted great interest, since novel application trends have emerged due to the great diversity of recent information generated on EPSs properties. HoPs have been synthesized by fermentation using bacterial cells and a cell-free enzymatic process, while HePs have been produced only by fermentation. The analysis of the EPSs production processes indicates that macronutrients such as the carbon and nitrogen source used in the culture media are very important for the synthesis of EPSs and the enzymes involved, understanding their importance can assist to design processes for production of EPSs with desirable characteristics and yields according to the needs of the processes and products to which they are applicable. This review emphasized in the analyses of carbon and nitrogen sources used for EPSs production and their functional applications and productive aspects.
Keywords: Exopolysaccharides, homopolysaccharides, heteropolysaccharides, lactic acid bacteria, extracellular enzymes.
|
|
 |

