 |
|
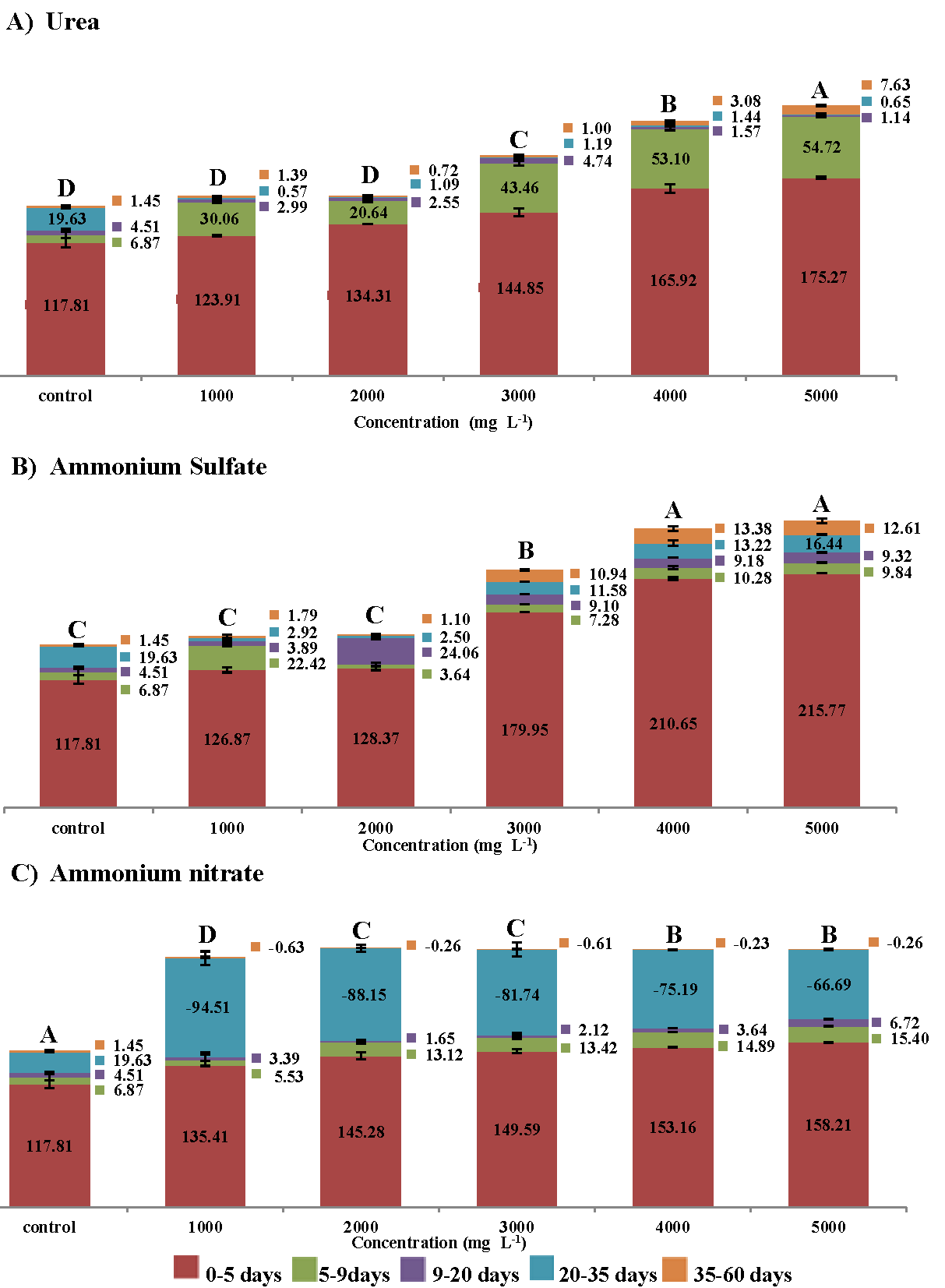
In this present study, the effect of different nitrogen sources in the anaerobic digestion of cheese whey on methane production, free ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide. The results showed that supplementation with urea at a concentration of 1000 mg L-1 the maximum methane production values of 513.95 ± 2.12 mL CH4 g VS-1 were obtained. On the other hand, supplementation with ammonium nitrate at a concentration of 1000 mg L-1 gave a value of methane of 415.93 ± 5.44 mL CH4 g VS-1 and exhibited the lowest values hydrogen sulfide of 267.69 ± 0.37 ppm and free ammonium of 49.18 ± 9.66 mg L-1. Supplementation with ammonium sulfate at a concentration of 2000 mg L-1, methane values of 466.64 ± 9.93 mL CH4 g VS-1 and hydrogen sulfide of 2768.43 ± 20.52 ppm were obtained. The findings from this research contributed to elucidate the role of supplementation with urea, ammonium sulfate, and ammonium nitrate in the anaerobic digestion process, which could help to solve some problems related to the reduction of methane production in cheese whey fed biodigesters.
Keywords: Anaerobic digestion, free ammonium, hydrogen sulfide, methane, nitrogen sources.
|
|
 |

