Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 20, No. 3 (2021), Cat1852
Decreasing the value of the cell potential using nPt/C|Ti and RuO2|Ti as cathodes in a reactor for electro leaching of electronic e-waste
|
J.C. Ramírez-Castellanos, M. Luna-Trujillo, V.E. Reyes-Cruz, A. Manzo-Robledo, G. Urbano-Reyes, M.A. Veloz-Rodríguez, J.C. Juarez-Tapia, J.A. Cobos-Murcia
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Cat1852
Abstract
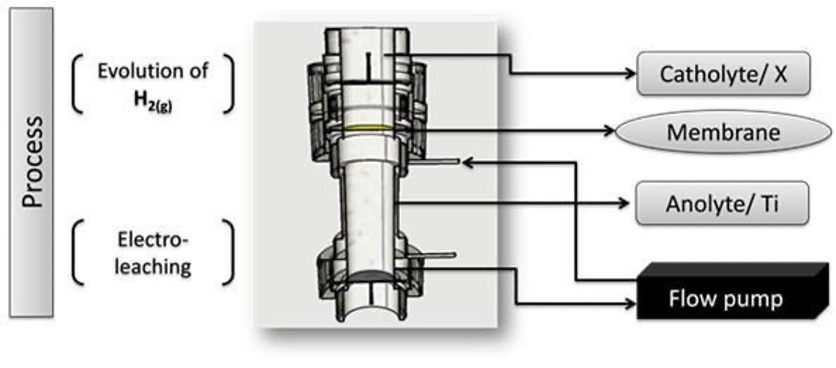 |
|
This work has to purpose decrease the value of the cell potential (Ecell) of an electrochemical reactor with a separate compartment with an anionic membrane designed for electro-leaching electronic waste (E-waste). In the anodic compartment using a titanium plate in HNO3 as an anolyte, while the electro-leaching of the metals and the evaluation of the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) was studied. Three different cathodes (Platinum; Pt, titanium coated with ruthenium oxide; RuO2|Ti and titanium coated with platinum nanoparticles; nPt/C|Ti) were used for the catalysis of the evolution reaction of hydrogen (HER) in a solution of H2SO4. The results obtained by voltammetry indicate that the electrodes modified with RuO2 and nPt/C, promote a greater cathodic current for the HER, decreasing the cell potential and increase the current density of the induced metallic electro-leaching. This implies the decrease of the electrical power that the reactor requires during its operation. Obtaining Space-time yield (STY) values of 123.4 and 64 mol·L-1·h-1·cm-2 for the carbon and platinum nanoparticle and the ruthenium oxide catalysts respectively.
Keywords: Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, E-waste, Electroleaching, STY, Electrochemical reactor.
|
|
 |

