 |
|
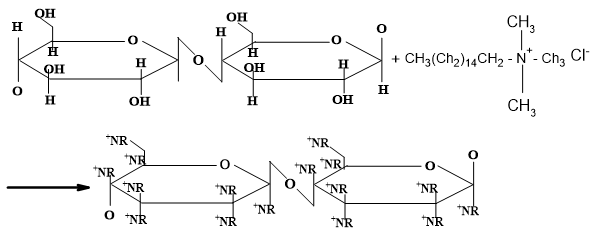
Adsorbents from the wheat husk (WH), wheat husk cellulose (WHC) and the cellulose modified with Cetyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (MWHC), in the removal of Congo Red were evaluated. Experiments were carried out in batch at different concentrations (40, 70 and 100 mg/L) and adsorbent doses (15, 25 and 35 mg), following a multifactorial 33 design of experiments. It was found the adsorption efficiency of Congo red increased with initial concentration and decrease in adsorbent dosage using all adsorbents. WHC and MWHC showed a rapid adsorption rate in the initial minutes of the process, reaching equilibrium at 480 and 120, respectively. The adsorption equilibrium on WHC and MWHC was described by the Freundlich model; showing this affinity: MWHC > WHC > WH. It was concluded wheat residues are a good precursor for the preparation of efficient adsorbents to remove Congo Red. CTAC functions as an adsorbent modifying agent for use in the removal of anionic contaminants. These results have a potential application in the treatment of wastewater from industries such as food and textiles.
Keywords: adsorption, Congo red dye, isotherms, wheat hulls
.
|
|
 |

